Amazon Sage Maker
Sage Maker Built-in Algorithms
Linear Learner
Linear Learner is a supervised learning algorithm that can be used for both classification and regression tasks. It's a simple yet powerful algorithm that works well for high-dimensional, sparse data.
-
Key Features:
- Linear Models: It supports both linear regression and binary/multiclass classification.
- Automatic Tuning: It automatically tunes the model complexity based on the input data.
- Scalability: It can handle large datasets and is optimized for distributed training.
- Built-in Loss Functions: It supports a variety of loss functions like logistic loss, hinge loss, and squared loss.
- Regularization: It supports L1 and L2 regularization to prevent overfitting.
- Real-time Predictions: It can be deployed as a real-time endpoint for making predictions.
-
input:
- RecordIO
- CSV
- File or Pipe mode both supported
-
How is it used:
- Preprocessing
- Training data must be normalized so all features have the same scale.
- Linear Learner automatically normalizes the data.
- Input data must be shuffled and split into mini-batches.
- Training
- Linear Learner uses stochastic gradient descent (SGD) to optimize the model parameters.
- It automatically tunes the learning rate and other hyperparameters.
- Validation
- Linear Learner uses the validation data to monitor the model's performance and prevent overfitting.
- It can automatically stop training if the model's performance degrades.
- Preprocessing
-
Important Hyperparameter
- Balance_multicast_weights
- learning_rate,mini_batch_size,use_bias
- L1
- target_precision
- Use with binary_classifier_model_selection_criteriaset to recall_at_target_precision
- Holds precision at this value while maximizing recall
- target_recall
- Use with binary_classifier_model_selection_criteriaset to precision_at_target_recall
- Holds recall at this value while maximizing precision
-
Instance Types
- Training
- Single or Multi CPU or GPU instance
- Multi-Gpu Does not help
- Training
XGBoost
XGBoost is a popular supervised learning algorithm that's known for its speed and performance. It's an implementation of gradient boosted decision trees designed for speed and performance. It's widely used in machine learning competitions and is known for its accuracy and speed.
-
Key Features:
- Speed: It's optimized for speed and can handle large datasets.
- Performance: It's known for its accuracy and performance.
- Regularization: It supports L1 and L2 regularization to prevent overfitting.
- Customizable: It supports a variety of hyperparameter to customize the model.
- Classification and Regression: It supports both classification and regression tasks.
-
input:
- libsvm
- CSV
- RecordIO
- Parquet
-
How is it used:
- Models are serialized/deserialized using pickle
- can use as Framework withing SageMaker
-
Important Hyperparameter
- num_round : Number of boosting rounds
- max_depth : Maximum depth of the tree
- eta : Learning rate can be used to prevent overfitting
- gamma : Minimum loss reduction required to make a further partition on a leaf node of the tree
- min_child_weight : Minimum sum of instance weight needed in a child
- subsample : Subsample ratio of the training instances
- colsample_bytree : Subsample ratio of columns when constructing each tree
- colsample_bylevel : Subsample ratio of columns for each level
- lambda : L2 regularization term on weights
- alpha : L1 regularization term on weights
- scale_pos_weight : Control the balance of positive and negative weights, useful for unbalanced classes
-
Instance Types
- If your task is memory-bound and not compute-bound, consider using M5 instances.
- XGBoost 1.2 introduced single-instance GPU training, available on P2, P3 instances. Set
tree_methodhyperparameter togpu_histfor faster and cost-effective training. - XGBoost 1.2-2 supports P2, P3, G4dn, G5 instances.
- XGBoost 1.5+ offers distributed GPU training; set
use_dask_gpu_trainingto true and distribution tofully_replicatedin TrainingInput. Note: Only works with csv or parquet input.
Seq2Seq
Seq2Seq is a supervised learning algorithm that's used for sequence-to-sequence tasks like machine translation, text summarization, and speech recognition. It's based on recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and is known for its ability to handle variable-length sequences.

-
Key Features:
- Sequence-to-Sequence: It's designed for sequence-to-sequence tasks like machine translation and text summarization.
- Recurrent Neural Networks: It's based on RNNs and can handle variable-length sequences.
- Customizable: It supports a variety of hyperparameters to customize the model.
- Bidirectional RNNs: It supports bidirectional RNNs to capture context from both directions.
- Attention Mechanism: It supports attention mechanisms to focus on relevant parts of the input sequence.
-
input:
-
RecordIO-Protobuf
- Tokens must be integers (this is unusual, since most algorithms want floating point data.)
-
Start with tokenized text files
-
Convert to protobufusing sample code
- Packs into integer tensors with vocabulary files
- A lot like the TF/IDF lab we did earlier.
-
Must provide training data, validation data, and vocabulary files.
-
-
How is it used:
- Preprocessing
- Tokenize the input sequences and convert them to integer tensors.
- Pad the sequences to the same length.
- Convert the sequences to RecordIO-Protobuf format.
- Training
- Seq2Seq uses RNNs to learn the relationship between input and output sequences.
- It uses teacher forcing to train the model to predict the next token in the output sequence.
- Validation
- Seq2Seq uses the validation data to monitor the model's performance and prevent overfitting.
- It can automatically stop training if the model's performance degrades.
- Preprocessing
-
Important Hyperparamters
- num_layers : Number of RNN layers
- hidden_dim : Dimension of the hidden state
- dropout : Dropout rate
- learning_rate : Learning rate
- batch_size : Batch size
- max_seq_len : Maximum sequence length
- attention_type : Attention mechanism type
- bidirectional : Use bidirectional RNNs
- use_masking : Use masking to handle variable-length sequences
-
Instance Types
- Training
- Single GPU instance only
- Multi-Gpu Does not help
- Training
DeepAR
DeepAR is a supervised learning algorithm that's used for time series forecasting. It's based on recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and is known for its ability to handle variable-length sequences.

-
Key Features:
- Time Series Forecasting: It's designed for time series forecasting tasks like sales forecasting and demand forecasting.
- Recurrent Neural Networks: It's based on RNNs and can handle variable-length sequences.
- Customizable: It supports a variety of hyperparameters to customize the model.
- Probabilistic Forecasting: It supports probabilistic forecasting to capture uncertainty in the predictions.
- Autoregressive Model: It supports autoregressive models to capture the temporal dependencies in the time series.
-
input:
- JSON lines format 1. Gzip or Parquet - Each Record is must have a timestamp and target value 1. Can have additional features - Must provide training data, validation data, and test data. -
How is it used:
- Always include entire time series for training, testing, and inference
- Use entire dataset as training set, remove last time points for testing. Evaluate on withheld values.
- Don’t use very large values for prediction length (> 400)
- Train on many time series and not just one when possible
- Use a large context length to capture long-term dependencies
-
Important Hyperparameter
- context_length : Length of the context
- prediction_length : Length of the prediction
- num_layers : Number of RNN layers
- hidden_dim : Dimension of the hidden state
- dropout : Dropout rate
- learning_rate : Learning rate
- batch_size : Batch size
- likelihood : Likelihood function
- cardinality : Cardinality of the categorical features
- embedding_dimension : Dimension of the categorical embeddings
-
Instance Types
- Training
- Single GPU instance only
- Single or Multi CPU instance
- CPU-only for inference
- May not need GPU for training
- Training
BlazingText
 BlazingText is a supervised learning algorithm that's used for word embeddings and text classification tasks. It's based on the Word2Vec algorithm and is known for its speed and scalability.
BlazingText is a supervised learning algorithm that's used for word embeddings and text classification tasks. It's based on the Word2Vec algorithm and is known for its speed and scalability.
-
Key Features:
- Word Embeddings: It can be used to generate word embeddings, which are dense vector representations of words.
- Text Classification: It supports text classification tasks like sentiment analysis and topic classification.
- Speed and Scalability: It's optimized for speed and can handle large datasets.
- Customizable: It supports a variety of hyperparameter to customize the model.
-
Input:
- Text data in RecordIO or CSV format.
-
How is it used:
- Preprocessing: Text data is tokenized and converted to integer tensors.
- Training: BlazingText uses the Word2Vec algorithm to learn word embeddings and a classification model.
- Validation: BlazingText uses the validation data to monitor the model's performance and prevent overfitting.
-
Important Hyperparameter:
- mode: The mode of operation (e.g., "continuous_bag_of_words" or "skip_gram").
- vector_dim: The dimension of the word embeddings.
- learning_rate: The learning rate for the model.
- batch_size: The batch size for training.
-
Instance Types:
- Training: Single or multi-GPU instances.
- Inference: CPU instances.
Object2Vec
 Object2Vec is an unsupervised learning algorithm that's used for generating vector representations of objects in a graph or network. It's based on the Word2Vec algorithm and is known for its ability to capture the relationships between objects.
Object2Vec is an unsupervised learning algorithm that's used for generating vector representations of objects in a graph or network. It's based on the Word2Vec algorithm and is known for its ability to capture the relationships between objects.
-
Key Features:
- Object Embeddings: It can be used to generate vector representations of objects in a graph or network.
- Capture Relationships: It can capture the relationships between objects based on their connections in the graph.
- Scalability: It's designed to handle large graphs and networks.
- Customizable: It supports a variety of hyperparameters to customize the model.
-
Input:
- Graph data in a supported format (e.g., CSV, JSON).
-
How is it used:
- Preprocessing: Graph data is converted to a suitable format for Object2Vec.
- Training: Object2Vec uses the Word2Vec algorithm to learn object embeddings based on the graph structure.
- Validation: Object2Vec can use a validation set to monitor the model's performance.
-
Important Hyperparameters:
- vector_dim: The dimension of the object embeddings.
- learning_rate: The learning rate for the model.
- batch_size: The batch size for training.
- window_size: The size of the context window around each object.
-
Instance Types:
- Training: Single or multi-GPU instances.
- Inference: CPU instances.
Object Detection
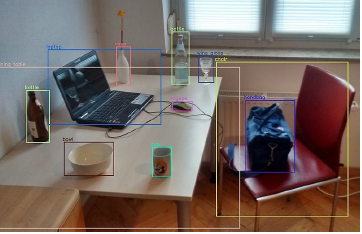
Object Detection is a computer vision algorithm that's used for detecting and locating objects in images or videos. It's based on deep learning techniques and is widely used in applications like self-driving cars, surveillance systems, and image analysis.
-
Key Features:
- Object Detection: It can detect and locate multiple objects in an image or video.
- Bounding Boxes: It provides bounding boxes around the detected objects, along with their class labels.
- Deep Learning: It's based on deep learning techniques like convolutional neural networks (CNNs).
- Transfer Learning: It supports transfer learning, allowing pre-trained models to be fine-tuned on new datasets.
-
Input:
- Images or videos in a supported format (e.g., PNG, JPEG, MP4).
-
How is it used:
- Preprocessing: Images or videos are resized and normalized for input to the model.
- Training: Object Detection models are trained on labeled datasets of images with bounding boxes and class labels.
- Validation: The model's performance is evaluated on a validation set using metrics like precision, recall, and mean Average Precision (mAP).
-
Important Hyperparameters:
- batch_size: The batch size for training.
- learning_rate: The learning rate for the model.
- optimizer: The optimization algorithm used for training (e.g., SGD, Adam).
- backbone_model: The pre-trained CNN model used as the backbone (e.g., ResNet, VGG).
-
Instance Types:
- Training: Single or multi-GPU instances.
- Inference: Single GPU instances or CPU instances (depending on the required performance).
Image Classification
Image Classification is a computer vision algorithm that's used for classifying images into predefined categories or classes. It's based on deep learning techniques and is widely used in applications like image recognition, content moderation, and medical imaging.

-
Key Features:
- Image Classification: It can classify images into predefined categories or classes.
- Deep Learning: It's based on deep learning techniques like convolutional neural networks (CNNs).
- Transfer Learning: It supports transfer learning, allowing pre-trained models to be fine-tuned on new datasets.
- Scalability: It can handle large datasets and is optimized for distributed training.
-
Input:
- Images in a supported format (e.g., PNG, JPEG).
-
How is it used:
- Preprocessing: Images are resized and normalized for input to the model.
- Training: Image Classification models are trained on labeled datasets of images with class labels.
- Validation: The model's performance is evaluated on a validation set using metrics like accuracy, precision, and recall.
-
Important Hyperparameters:
- batch_size: The batch size for training.
- learning_rate: The learning rate for the model.
- optimizer: The optimization algorithm used for training (e.g., SGD, Adam).
- backbone_model: The pre-trained CNN model used as the backbone (e.g., ResNet, VGG).
-
Instance Types:
- Training: Single or multi-GPU instances.
- Inference: Single GPU instances or CPU instances (depending on the required performance).
Semantic Segmentation
Semantic Segmentation is a computer vision algorithm that's used for segmenting an image into different regions or objects, assigning a class label to each pixel. It's based on deep learning techniques and is widely used in applications like self-driving cars, medical imaging, and image analysis.

-
Key Features:
- Pixel-level Segmentation: It can segment an image into different regions or objects, assigning a class label to each pixel.
- Deep Learning: It's based on deep learning techniques like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and encoder-decoder architectures.
- Transfer Learning: It supports transfer learning, allowing pre-trained models to be fine-tuned on new datasets.
- Scalability: It can handle large datasets and is optimized for distributed training.
-
Input:
- Images in a supported format (e.g., PNG, JPEG).
-
How is it used:
- Preprocessing: Images are resized and normalized for input to the model.
- Training: Semantic Segmentation models are trained on labeled datasets of images with pixel-level annotations.
- Validation: The model's performance is evaluated on a validation set using metrics like mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) and pixel accuracy.
-
Important Hyperparameters:
- batch_size: The batch size for training.
- learning_rate: The learning rate for the model.
- optimizer: The optimization algorithm used for training (e.g., SGD, Adam).
- backbone_model: The pre-trained CNN model used as the backbone (e.g., ResNet, VGG).
- encoder_decoder_architecture: The encoder-decoder architecture used for the segmentation model (e.g., U-Net, Mask R-CNN).
-
Instance Types:
- Training: Single or multi-GPU instances.
- Inference: Single GPU instances or CPU instances (depending on the required performance).
Random Cut Forest
Random Cut Forest is an unsupervised learning algorithm that's used for anomaly detection and data outlier detection. It's based on the concept of decision trees and is known for its ability to handle high-dimensional data and its robustness to noise.
-
Key Features:
- Anomaly Detection: It can be used to detect anomalies or outliers in data.
- Unsupervised Learning: It does not require labeled data for training.
- High-Dimensional Data: It can handle high-dimensional data efficiently.
- Robustness: It's robust to noise and missing values in the data.
-
Input:
- Tabular data in a supported format (e.g., CSV, RecordIO).
-
How is it used:
- Preprocessing: Data is preprocessed and normalized, if necessary.
- Training: Random Cut Forest builds an ensemble of decision trees by randomly partitioning the data and creating trees based on the partitions.
- Inference: New data points are scored based on their similarity to the trees in the ensemble, with lower scores indicating potential anomalies.
-
Important Hyperparameters:
- num_trees: The number of trees in the ensemble.
- sample_size: The size of the sample used for building each tree.
- num_dimensions_per_node: The number of dimensions to consider for splitting at each node.
- shingle_dim: The dimension used for creating data shingles (used for handling missing values).
-
Instance Types:
- Training: Single or multi-CPU instances.
- Inference: Single CPU instances.
LDA (Latent Dirichlet Allocation)
LDA is an unsupervised learning algorithm that's used for topic modeling, which involves discovering the underlying topics or themes in a collection of documents. It's based on a probabilistic model and is widely used in applications like text analysis, information retrieval, and content recommendation.

-
Key Features:
- Topic Modeling: It can be used to discover the underlying topics or themes in a collection of documents.
- Unsupervised Learning: It does not require labeled data for training.
- Probabilistic Model: It's based on a probabilistic model that represents each document as a mixture of topics.
- Scalability: It can handle large collections of documents.
-
Input:
- Text data in a supported format (e.g., CSV, RecordIO).
-
How is it used:
- Preprocessing: Text data is preprocessed, tokenized, and converted into a suitable format for LDA.
- Training: LDA learns the topic distributions and the word distributions for each topic based on the input documents.
- Inference: New documents can be mapped to the learned topics, and the topic distributions can be used for various applications.
-
Important Hyperparameters:
- num_topics: The number of topics to be learned by the model.
- alpha: The Dirichlet prior for the document-topic distribution.
- beta: The Dirichlet prior for the topic-word distribution.
- max_iterations: The maximum number of iterations for the model training.
-
Instance Types:
- Training: Single or multi-CPU instances.
- Inference: Single CPU instances.
KNN (K-Nearest Neighbors)
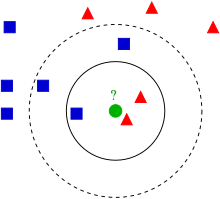 KNN is a supervised learning algorithm that's used for classification and regression tasks. It's a non-parametric algorithm that makes predictions based on the similarity or distance between the new data point and the existing data points in the training set.
KNN is a supervised learning algorithm that's used for classification and regression tasks. It's a non-parametric algorithm that makes predictions based on the similarity or distance between the new data point and the existing data points in the training set.
-
Key Features:
- Classification and Regression: It can be used for both classification and regression tasks.
- Non-parametric: It does not make any assumptions about the underlying data distribution.
- Similarity-based: Predictions are made based on the similarity or distance between data points.
- Interpretability: The algorithm is relatively simple and interpretable.
-
Input:
- Tabular data in a supported format (e.g., CSV, RecordIO).
-
How is it used:
- Preprocessing: Data is preprocessed and normalized, if necessary.
- Training: KNN stores the entire training dataset.
- Inference: For a new data point, KNN finds the k nearest neighbors based on a distance metric (e.g., Euclidean distance) and makes predictions based on the labels or values of those neighbors.
-
Important Hyperparameters:
- k: The number of nearest neighbors to consider for making predictions.
- distance_metric: The distance metric used to measure the similarity between data points (e.g., Euclidean, Manhattan, Cosine).
- weight_function: The function used to weight the contributions of the neighbors (e.g., uniform, distance-based).
-
Instance Types:
- Training: Single CPU instances.
- Inference: Single CPU instances.
K-Means Clustering
K-Means Clustering is an unsupervised learning algorithm that's used for clustering or partitioning data into K distinct groups or clusters. It's based on the idea of minimizing the sum of squared distances between data points and their assigned cluster centroids.
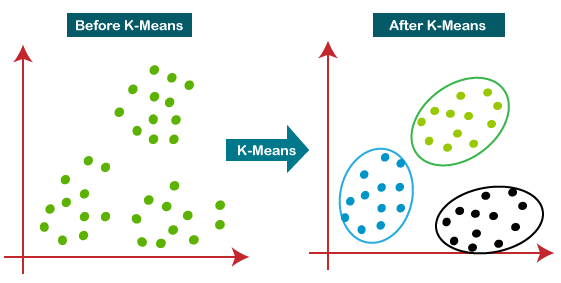
-
Key Features:
- Clustering: It can be used to group or cluster data points based on their similarities.
- Unsupervised Learning: It does not require labeled data for training.
- Iterative Optimization: It iteratively refines the cluster assignments and centroids to minimize the sum of squared distances.
- Scalability: It can handle large datasets and is optimized for distributed training.
-
Input:
- Tabular data in a supported format (e.g., CSV, RecordIO).
-
How is it used:
- Preprocessing: Data is preprocessed and normalized, if necessary.
- Training: K-Means Clustering initializes K cluster centroids and iteratively assigns data points to the nearest centroids and updates the centroids based on the assigned points.
- Inference: New data points can be assigned to the closest cluster based on their distances to the learned centroids.
-
Important Hyperparameters:
- k: The number of clusters to be formed.
- init_mode: The method used for initializing the cluster centroids (e.g., random, k-means++).
- max_iterations: The maximum number of iterations for the clustering algorithm.
- tolerance: The tolerance value used to determine convergence.
-
Instance Types:
- Training: Single or multi-CPU instances.
- Inference: Single CPU instances.
IP Insights
IP Insights is a machine learning algorithm provided by Amazon SageMaker that is used for detecting and classifying entities, such as names, locations, and organizations, within text data. It is based on natural language processing (NLP) techniques and can be useful for tasks like named entity recognition, text analysis, and information extraction.
-
Key Features:
- Entity Detection and Classification: It can detect and classify entities like names, locations, organizations, and more within text data.
- Pre-trained Models: It provides pre-trained models that can be fine-tuned on specific data or used out-of-the-box.
- Scalability: It can handle large volumes of text data and is optimized for distributed processing.
- Customizable: It supports fine-tuning the pre-trained models on custom data to improve performance for specific use cases.
-
Input:
- Text data in a supported format (e.g., CSV, JSON).
-
How is it used:
- Preprocessing: Text data is cleaned and preprocessed, if necessary.
- Training (Optional): The pre-trained models can be fine-tuned on custom data to improve performance for specific use cases.
- Inference: Text data is passed to the IP Insights model, which detects and classifies entities within the text.
-
Important Hyperparameters:
- model_type: The type of pre-trained model to use (e.g., BERT, DistilBERT).
- max_length: The maximum length of the input text sequence.
- batch_size: The batch size for inference.
- score_threshold: The confidence score threshold for entity detection.
-
Instance Types:
- Training (Fine-tuning): Single or multi-GPU instances.
- Inference: Single GPU instances or CPU instances (depending on the required performance).
PCA (Principal Component Analysis)
PCA is an unsupervised learning algorithm that is used for dimensionality reduction and feature extraction in machine learning. It is a technique that transforms high-dimensional data into a lower-dimensional space while retaining as much of the original data's variance as possible.
-
Key Features:
- Dimensionality Reduction: It can reduce the number of features or dimensions in the data while preserving the most important information.
- Feature Extraction: It can extract new, uncorrelated features from the original data.
- Visualization: It can be used for visualizing high-dimensional data in a lower-dimensional space.
- Noise Reduction: It can help reduce noise and redundancy in the data.
-
Input:
- Tabular data in a supported format (e.g., CSV, RecordIO).
-
How is it used:
- Preprocessing: Data is preprocessed and normalized, if necessary.
- Training: PCA calculates the principal components, which are the new dimensions or features that represent the most important information in the data.
- Inference: New data points can be projected onto the principal components to obtain their lower-dimensional representations.
-
Important Hyperparameters:
- n_components: The number of principal components to retain.
- whiten: Whether to perform whitening (normalization) on the principal components.
- svd_solver: The algorithm used for computing the singular value decomposition (e.g., 'auto', 'full', 'arpack').
-
Instance Types:
- Training: Single CPU instances.
- Inference: Single CPU instances.
PCA is often used as a preprocessing step for other machine learning algorithms, as it can help reduce the dimensionality of the data, which can improve the performance and efficiency of the algorithms while retaining the most important information.
Hyperparameter tuning
As you saw that each algorithm have it's on hyperparameter nobody can tell you the best hyperparameter for your model. So, you need to tune the hyperparameter to get the best model.
-
What is Hyperparameter Tuning?
- Hyperparameter tuning, also known as hyperparameter optimization, is the process of finding the best set of hyperparameters for a machine learning model.
-
Why is Hyperparameter Tuning Important?
- The performance of a machine learning model is highly dependent on the choice of hyperparameters.
Automatic Model Tuning Best Practices
When tuning your machine learning model automatically, follow these best practices:
1. Optimize Selectively
- Rule: Don't tweak too many settings at once.
- Explanation: Adjust a few hyperparameters at a time to understand their impact better.
2. Restrict Parameter Ranges
- Rule: Keep parameter ranges as narrow as possible.
- Explanation: Focusing on specific values enhances the efficiency of the tuning process.
3. Logarithmic Scales
- Rule: Use logarithmic scales when appropriate.
- Explanation: Logarithmic scaling helps explore a wide range of values, especially for parameters with large value ranges.
4. Manage Concurrent Jobs
- Rule: Limit the number of simultaneous training jobs.
- Explanation: Running too many jobs concurrently may hinder the learning process. Opt for a balanced approach.
5. Ensure Metric Consistency
- Rule: Confirm consistent reporting of objective metrics across multiple instances.
- Explanation: Accurate metrics ensure reliable evaluation of model performance, especially when utilizing multiple computing instances.
Remember, these practices contribute to a more effective and efficient automatic model tuning process.
Sage Maker and Spark
> Covered in the following
- Data LakesData LakesData Lake Introduction to data lakes Why Data Lakes? 1. Are a great way to store and analyze large volumes of data at a low cost. 1. Exponential growth of data. 1. unstructured data. - Text - Images - Videos - Audio 1. Need analytics faster - Days - Hours - Real time Benefits of Data Lakes Data warehouse vs Data Lake Data Lake Analytics Functionality vs Aws This Course will cover AWS Glue AWS Glue is a fully managed extract, transform, and load (ETL) ser
- Data EngineeringData EngineeringData Engineering S3 S3 Storage Classes S3 Standard**: For general-purpose storage of frequently accessed data; designed for durability of 99.999999999% of objects over a given year. S3 Intelligent-Tiering**: Designed to optimize costs by automatically moving data to the most cost-effective access tier, without performance impact or operational overhead. S3 Standard-IA**: For long-lived, infrequently accessed data that needs to be accessed rapidly when needed. S3 One Zone-IA**: For long-lived,
- Building Data AnalyticsBuilding Data AnalyticsBuilding Batch Data Analytics Solutions on AWS In this guide, we'll explore how to build batch data analytics solutions using Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce). Amazon EMR is a cloud-based big data platform that allows you to process large datasets efficiently. We'll cover various modules to help you understand the key components and best practices for designing and implementing batch analytics solutions. Module 1: Introduction to Amazon EMR What is Amazon EMR? Amazon EMR is a managed big data
SageMaker New Features
> Covered in the following
- Parctical Data ScienceParctical Data SciencePractical Data Science Common ML use cases - Classification: Predicting a category - Regression: Predicting a number - Clustering: Finding groups in data - Anomaly detection: Finding outliers ML model benefits identify patterns**: ML models can identify patterns in data that humans can't Minimize human error**: ML models can make predictions without human intervention Can become more accurate over time**: ML models can learn from new data and improve their predictions variety of data