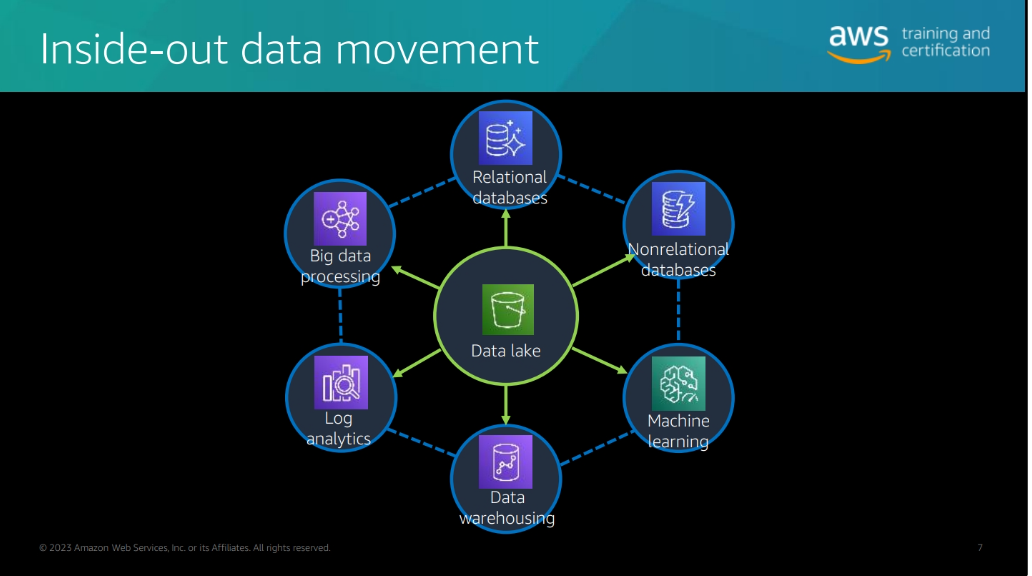
Data Lakes
Data Lake
Introduction to data lakes
Why Data Lakes?
- Are a great way to store and analyze large volumes of data at a low cost.
- Exponential growth of data.
- unstructured data.
- Text
- Images
- Videos
- Audio
- Need analytics faster
- Days
- Hours
- Real time
Benefits of Data Lakes
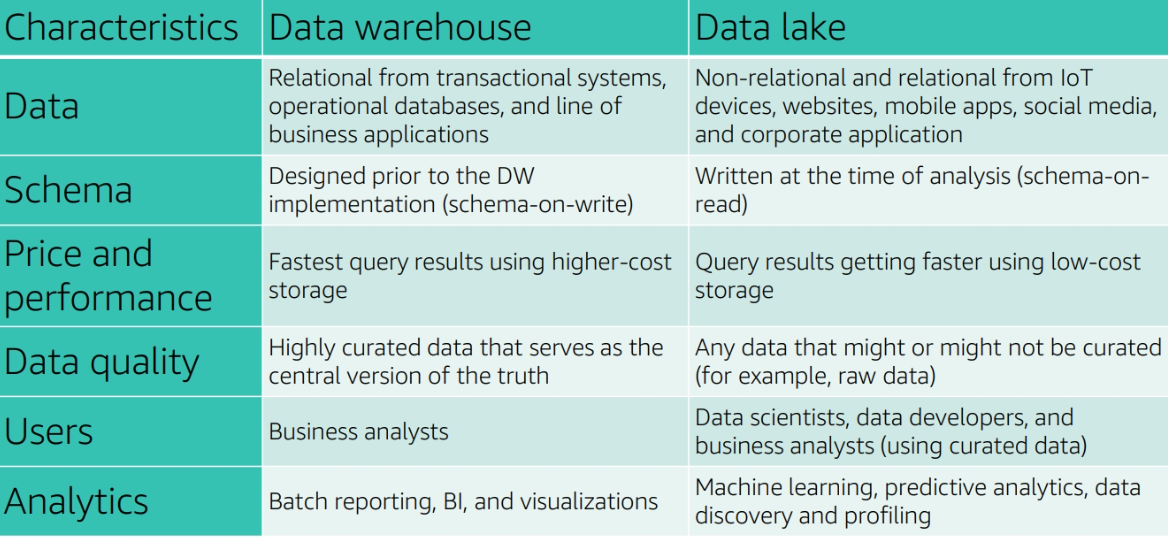
Data warehouse vs Data Lake
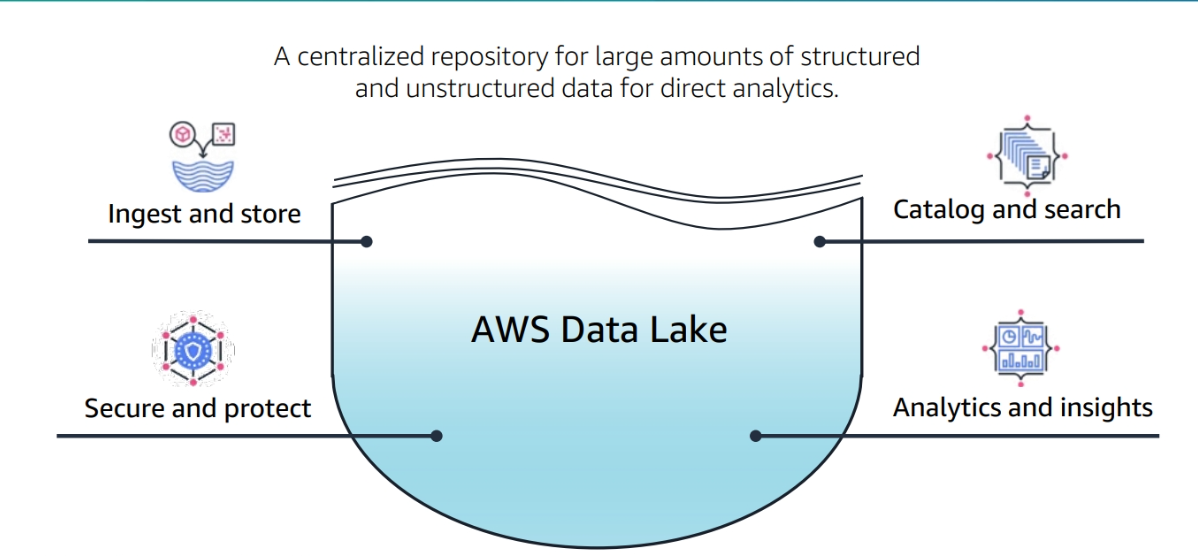
Data Lake
Analytics Functionality vs Aws
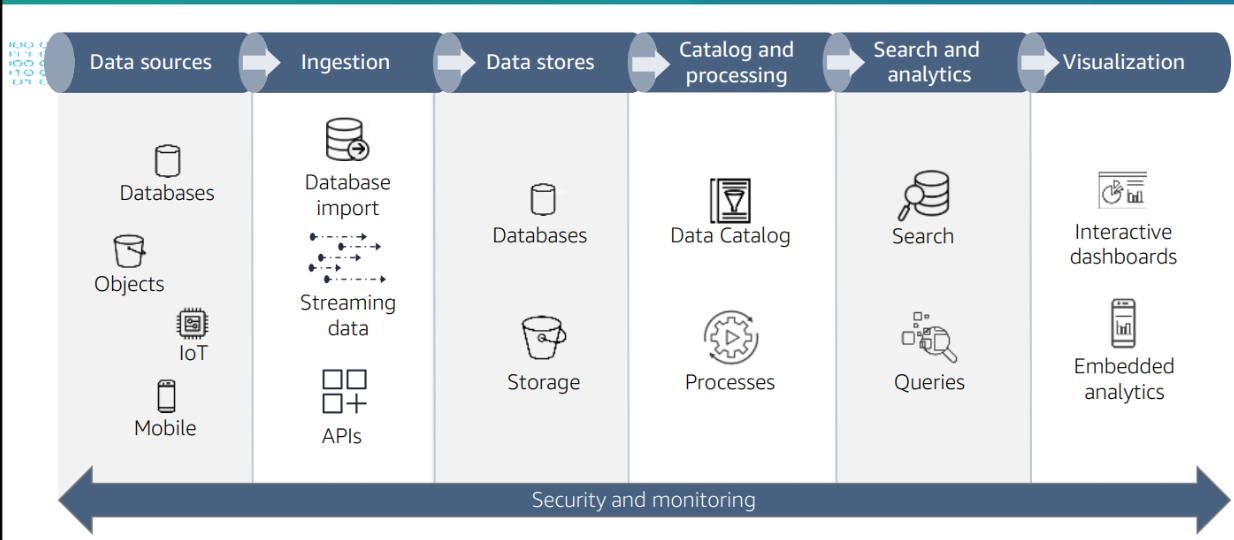
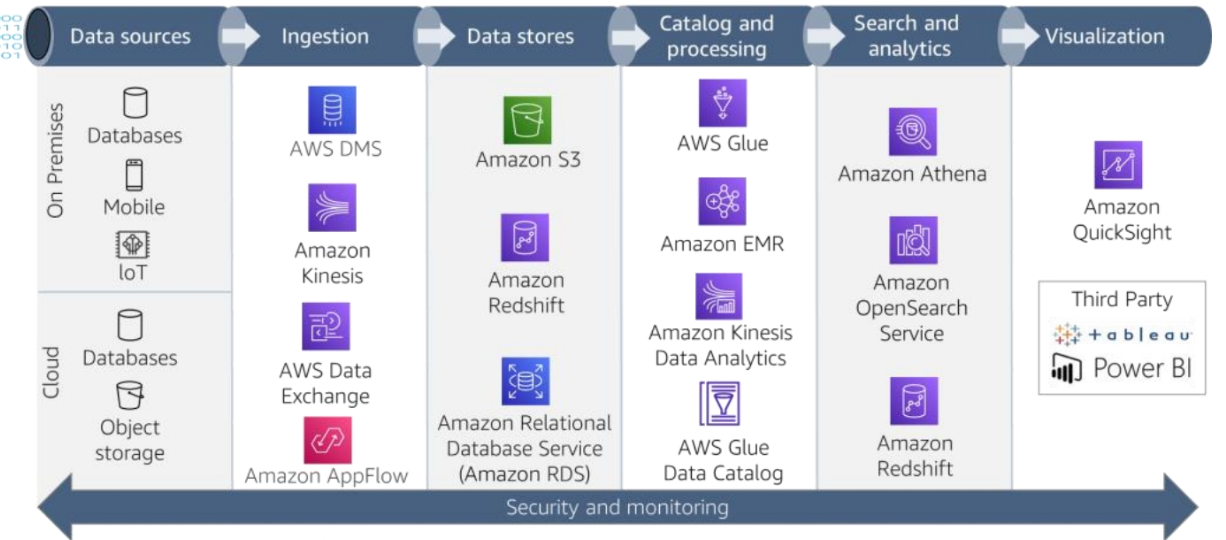
This Course will cover
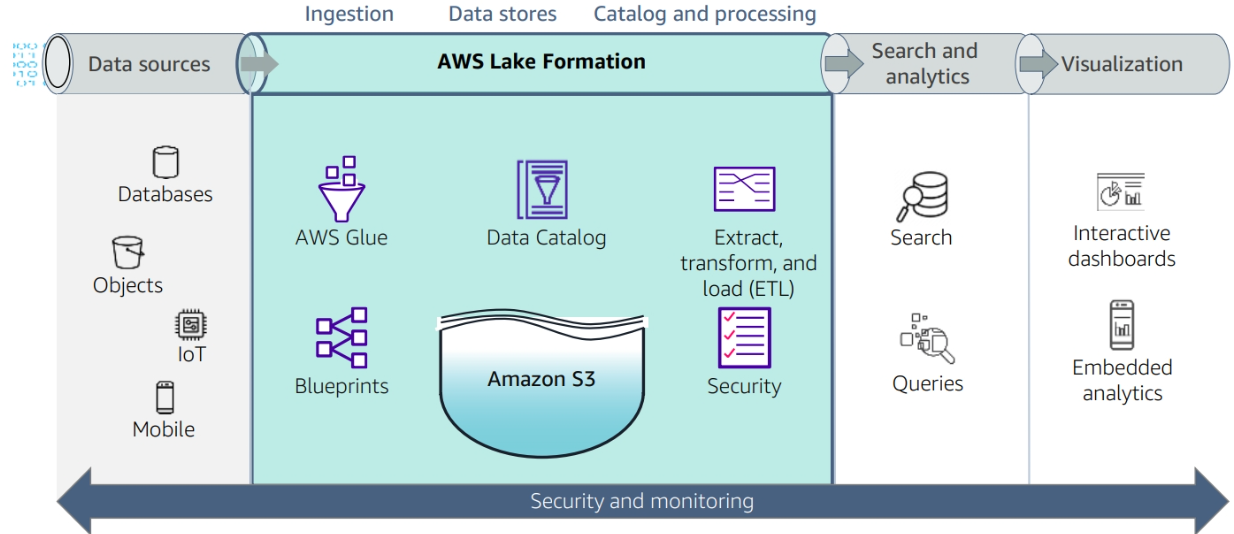
AWS Glue
AWS Glue is a fully managed extract, transform, and load (ETL) service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It is designed to simplify the process of preparing and loading data for analysis. AWS Glue automates the discovery, cataloging, and transformation of data from various sources, making it easier to move and combine datasets for analytics.
Key Features:
-
Data Catalog:
- AWS Glue includes a centralized metadata repository called the Data Catalog, where information about available data sources, transformations, and targets is stored.
- The Data Catalog provides a unified view of metadata, making it easier to discover and understand the structure of your data.
-
ETL Automation:
- With AWS Glue, you can create ETL jobs using a visual interface or by writing custom code in Python or Scala.
- The service automatically generates ETL code, reducing the need for manual coding and accelerating the ETL process.
-
Serverless Architecture:
- AWS Glue is a serverless service, meaning you don't need to provision or manage infrastructure. It scales dynamically based on the processing needs of your jobs.
-
Integration with Other AWS Services:
- AWS Glue seamlessly integrates with other AWS services, such as Amazon S3, Amazon Redshift, and Amazon RDS, allowing you to build end-to-end data workflows.
Data Catalog
The Data Catalog is a crucial component of AWS Glue, serving as a metadata repository that stores information about your data assets. It acts as a comprehensive catalog that facilitates the management, organization, and discovery of data. Here are some key aspects of the AWS Glue Data Catalog:
-
Metadata Storage:
- The Data Catalog stores metadata about tables, schemas, partitions, and transformations. This metadata provides a detailed understanding of the structure and characteristics of your data.
-
Unified View:
- By centralizing metadata in the Data Catalog, AWS Glue provides a unified view of your data assets. This makes it easier for data engineers, analysts, and scientists to discover and work with data across various sources.
-
Search and Discovery:
- Users can search for and discover relevant datasets using the Data Catalog. The metadata includes information about data sources, formats, and transformations, aiding in the exploration of available data.
-
Access Control:
- AWS Glue allows you to define access controls for the Data Catalog, ensuring that only authorized users can view or modify metadata. This helps in maintaining data security and compliance.
-
Integration with External Tools:
- The Data Catalog can be seamlessly integrated with external tools and services, enhancing the overall data governance and collaboration within your organization.
Data ingestion and cataloging
Storage of datasets
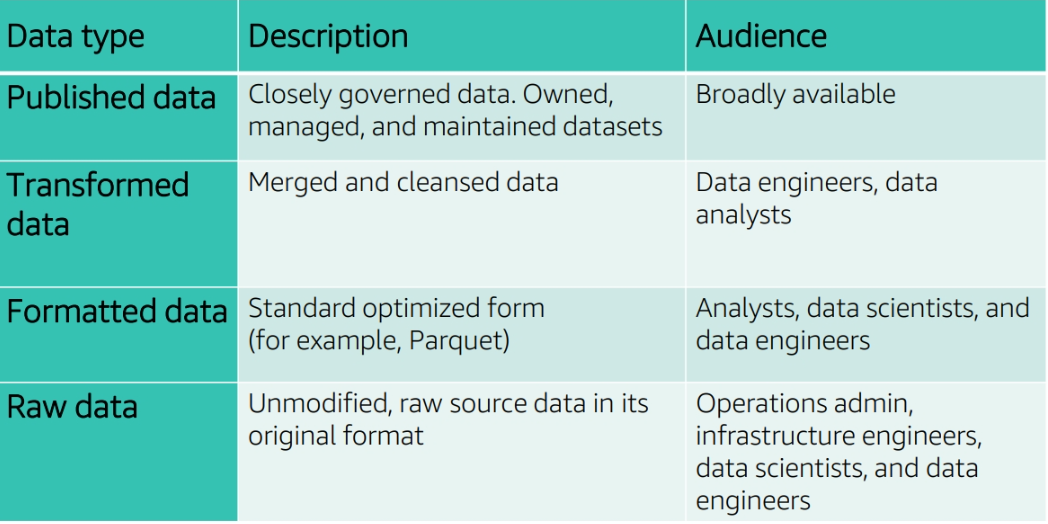
Difference between CSV and Parquet
1. Storage Format:
-
CSV: Stores data in plain text format with values separated by commas or other delimiters. It is a human-readable format but may not be as space-efficient as binary formats.
-
Parquet: Utilizes a columnar storage format, storing data in a highly compressed binary format. It organizes data into columns rather than rows, allowing for better compression and efficient storage.
2. Compression:
-
CSV: Generally has limited built-in compression. The compression is achieved mainly through general-purpose algorithms applied to the entire file.
-
Parquet: Uses advanced compression techniques, including dictionary encoding and run-length encoding, which can significantly reduce storage space. It allows for more efficient compression by compressing data within each column separately.
3. Schema Evolution:
-
CSV: Schema evolution (changing the structure of data over time) can be challenging, especially when dealing with large datasets, as the schema is not explicitly defined within the file.
-
Parquet: Supports schema evolution, making it easier to add, remove, or modify columns without the need for data conversion. This is particularly useful in evolving data architectures.
4. Performance:
-
CSV: Reading and writing CSV files can be slower, especially when dealing with large datasets, as the entire file must be processed sequentially.
-
Parquet: Due to its columnar storage and compression, Parquet is designed for high performance, especially for analytical queries that involve reading only specific columns. This makes it suitable for big data processing frameworks like Apache Spark and Apache Hive.
5. Data Types:
-
CSV: Generally supports basic data types (text, numbers), and the interpretation of data types may depend on how the data is imported or read.
-
Parquet: Supports a wide range of complex data types, including nested structures and custom types. This allows for more flexibility in representing diverse datasets.
6. Use Cases:
-
CSV: Suitable for simple, tabular data storage and exchange, especially when human readability is a priority.
-
Parquet: Ideal for big data processing, analytics, and data warehousing, where storage efficiency, fast query performance, and schema evolution are crucial.
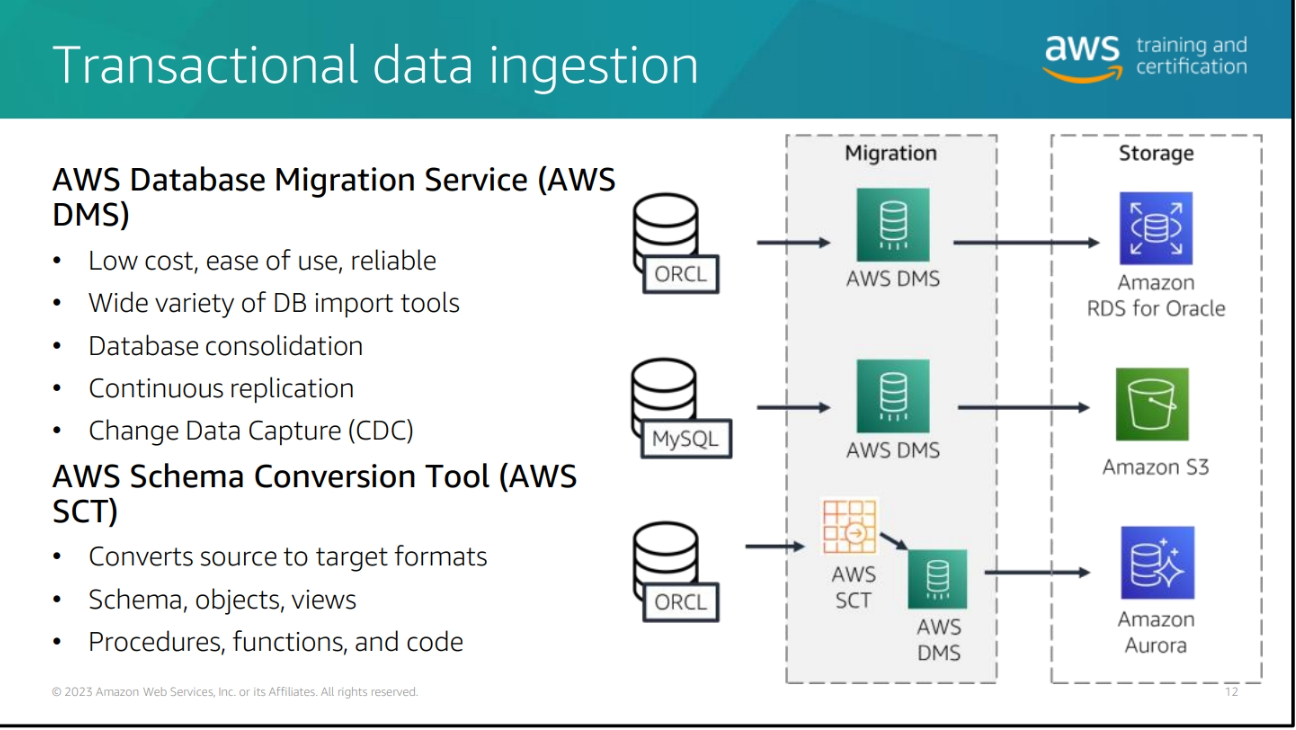
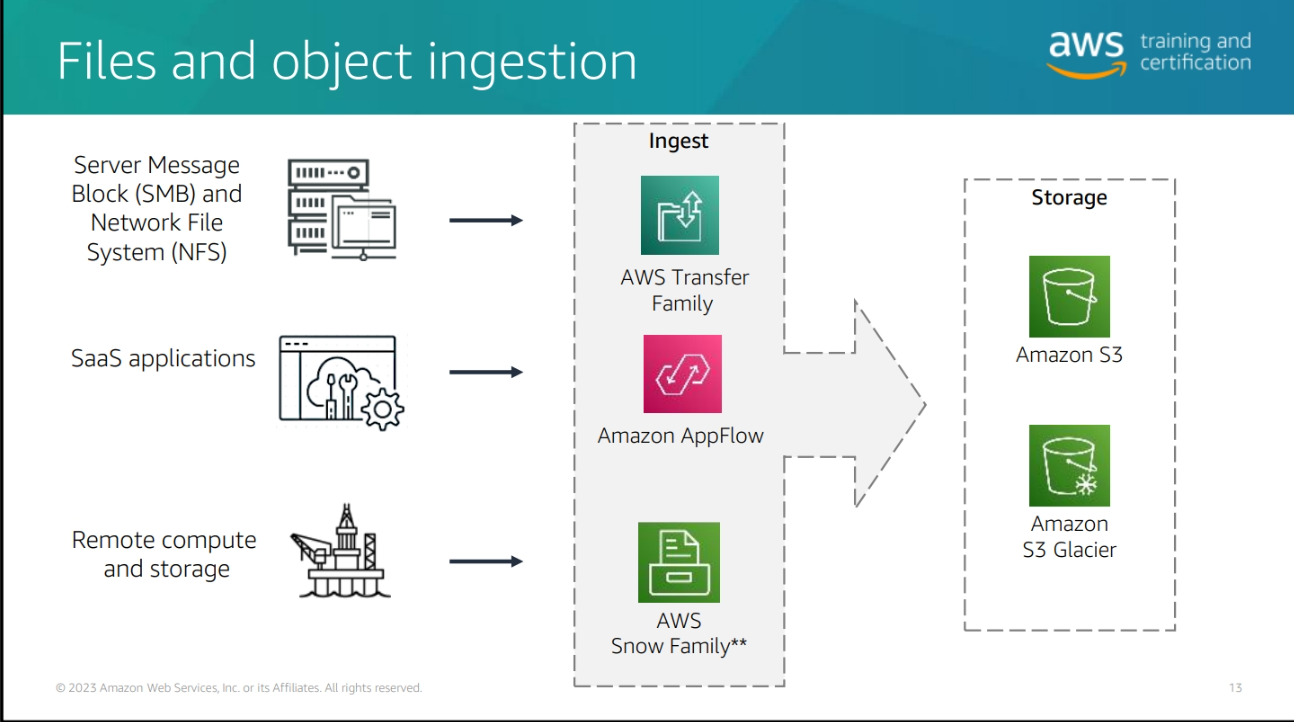
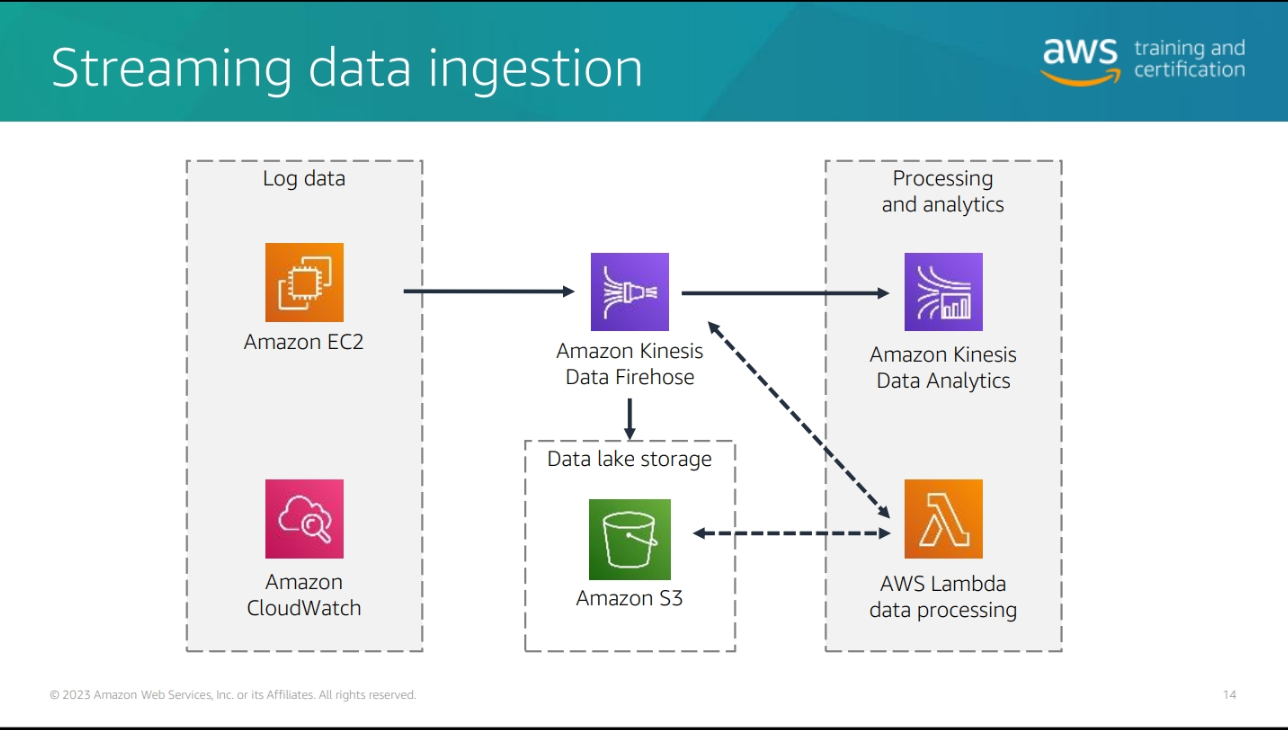
Difference type of data ingestion in AWS
Crawl and Catalogue data
AWS Glue consists of a central metadata repository known as the AWS Glue Data Catalog, an ETL engine that automatically generates Python or Scala code, and a flexible scheduler that handles dependency resolution, job monitoring, and retriesr
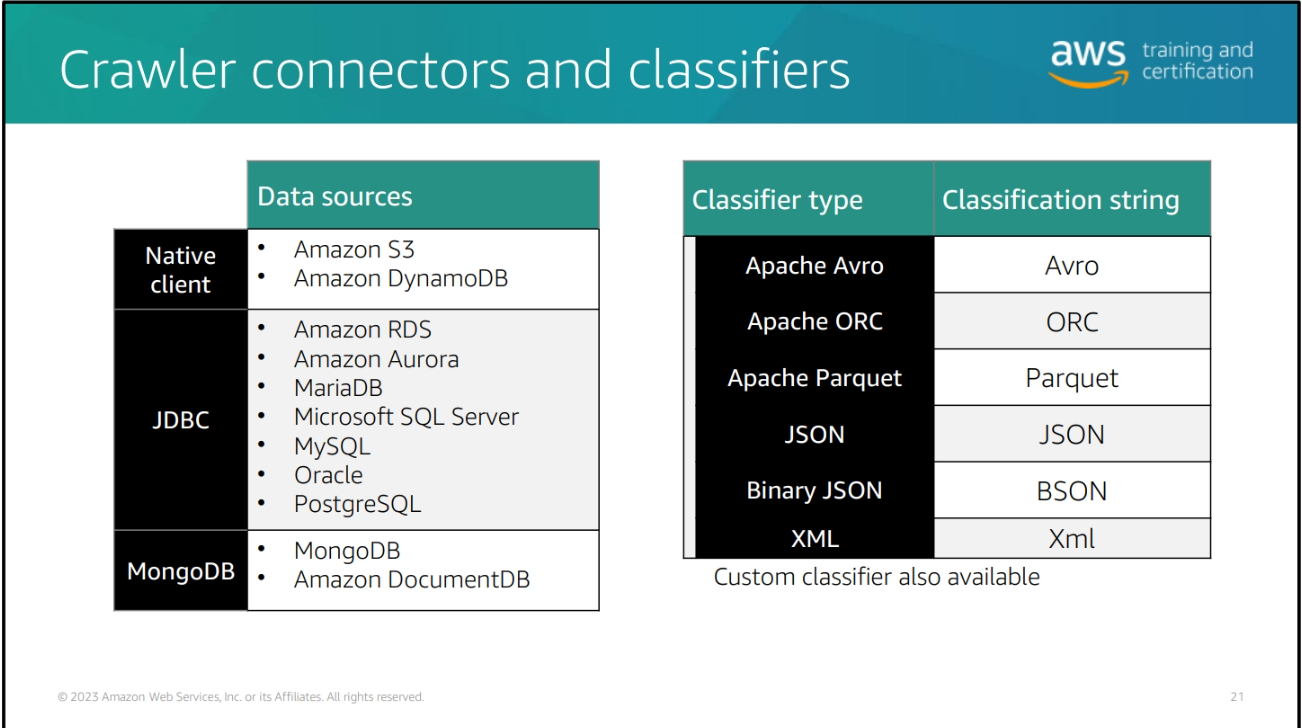
AWS Glue Data Catalog The AWS Glue Data Catalog provides a uniform repository where disparate systems can store and find metadata to keep track of data in the data lake. The catalog contains metadata describing and referencing the data lake stores and native storage location. When the data is cataloged, it is immediately available for search and query using Amazon Athena, Amazon EMR, and Amazon Redshift Spectrum.
AWS Glue Crawler AWS Glue Crawlers can scan data in all kinds of repositories, classify it, extract schema information from it, and store the metadata automatically in the AWS Glue Data Catalog. AWS Glue Studio is designed to work with both tabular and semi-structured data. Crawlers run as AWS Glue jobs and can be triggered by the scheduler component of AWS Glue.
Crawler
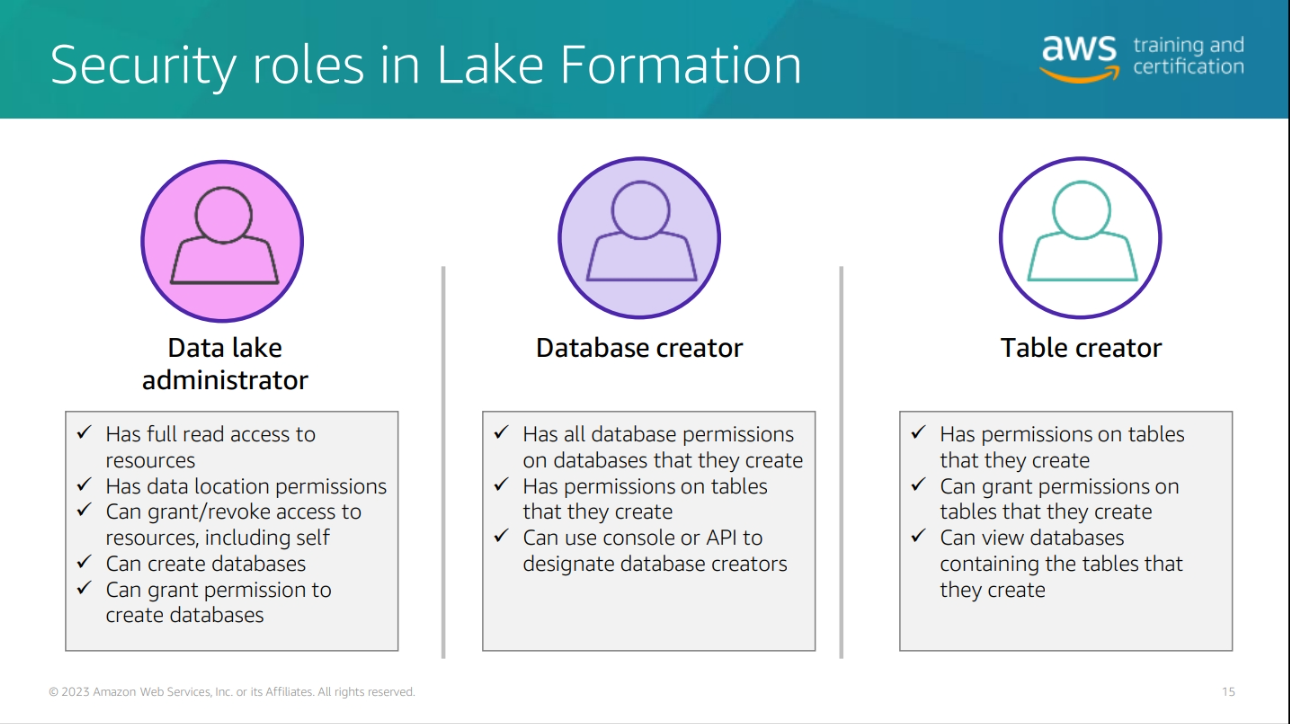
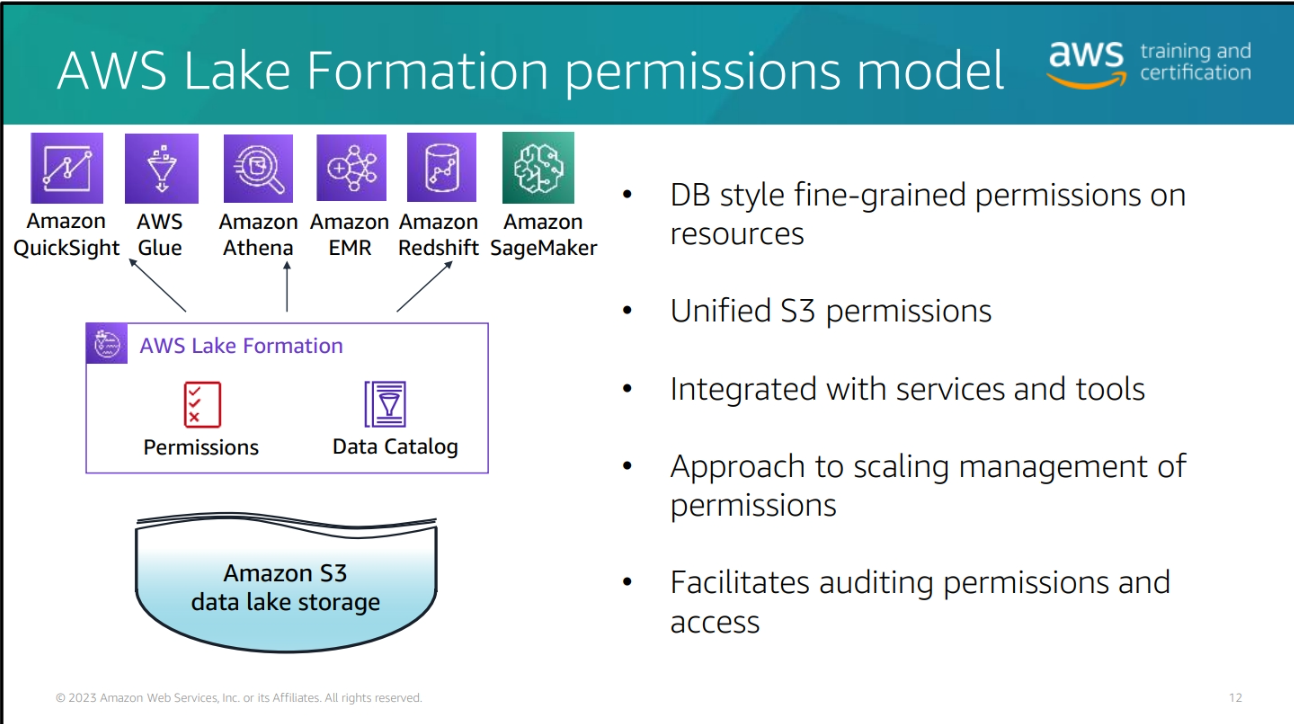
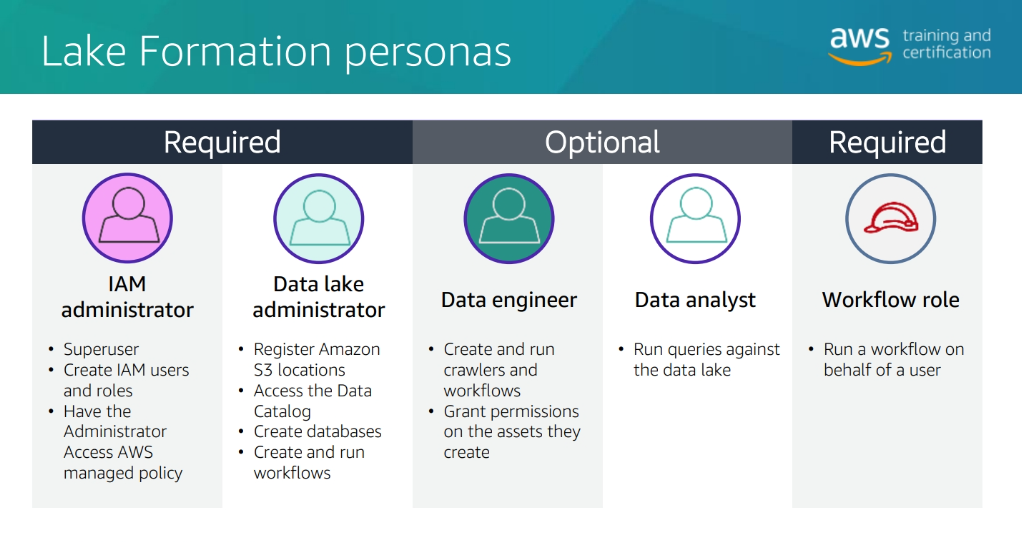
Building a data Lake with AWS Lake Formation
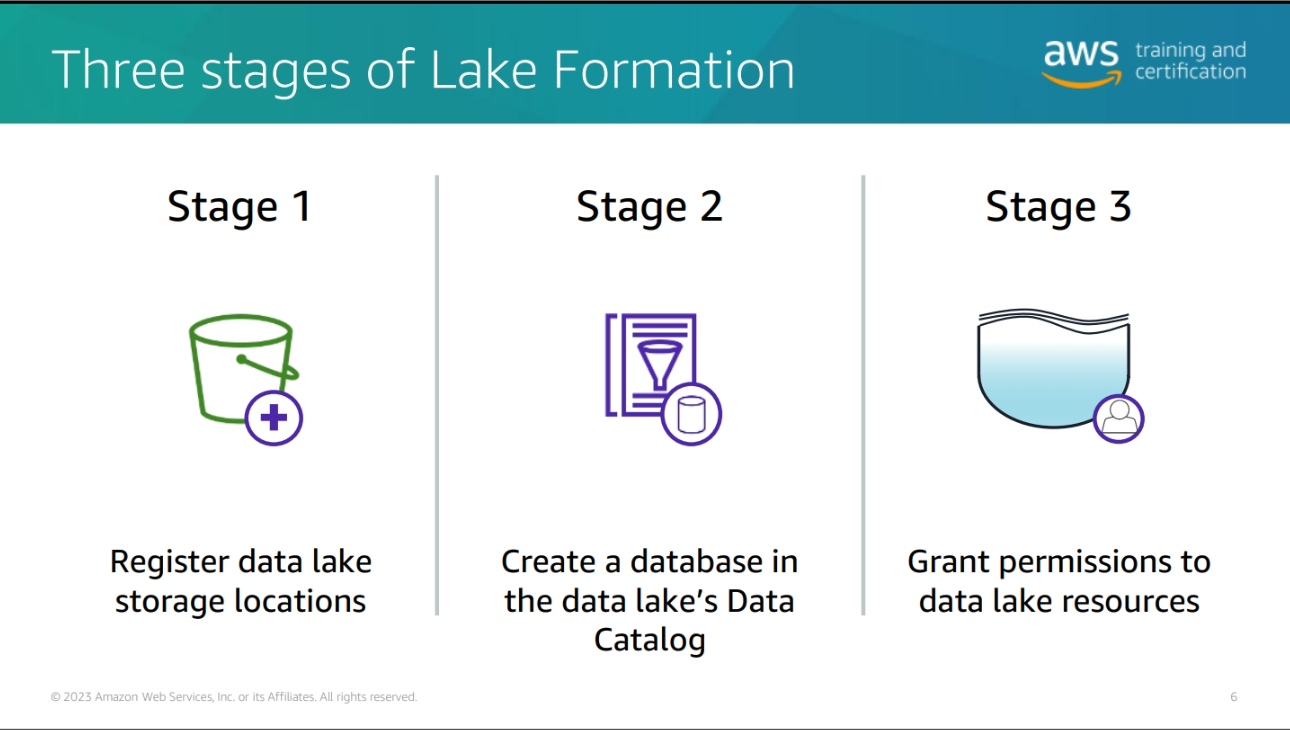

Data processing and analytics
Data preparation
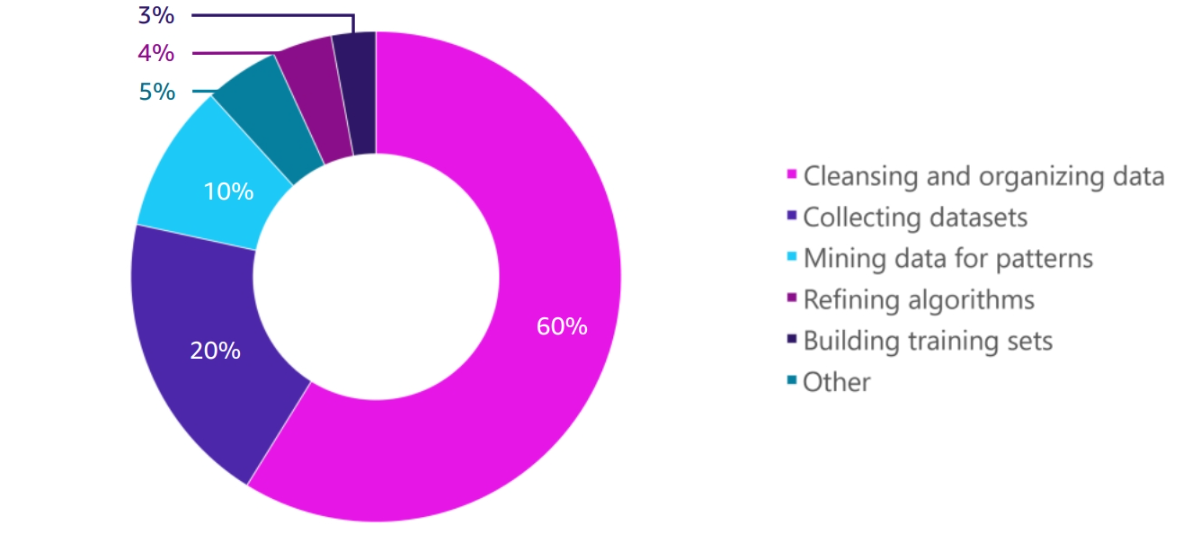
Data cleansing and preparation
Data cleansing is the process of identifying and correcting errors or inconsistencies in data to improve its quality. It involves various techniques to clean, transform, and standardize data, making it suitable for analysis and reporting. Here are some common data cleansing tasks:
1. Removing Duplicates:
- Description: Identifying and removing duplicate records from a dataset.
- Example: A customer database contains multiple entries for the same customer due to data entry errors or system issues.
- Techniques: Using SQL queries, data deduplication tools, or custom scripts to identify and eliminate duplicate records.
- Benefits: Reducing data redundancy, improving data accuracy, and ensuring consistency in reporting.
- Challenges: Identifying duplicates accurately, especially when dealing with large datasets or complex data structures.
- Tools: SQL, Python (pandas library), data deduplication software.
- Best Practices: Establishing unique identifiers for records, implementing data validation rules, and regularly monitoring data quality.
- Considerations: Balancing the need for data deduplication with the risk of losing valuable information.
2. Standardizing Data:
- Description: Converting data into a consistent format or structure to facilitate analysis and comparison.
- Example: Standardizing date formats, currency symbols, or units of measurement across different datasets.
- Techniques: Using data transformation functions, regular expressions, or lookup tables to standardize data elements.
- Benefits: Enhancing data uniformity, enabling accurate aggregation and reporting, and simplifying data integration.
- Challenges: Dealing with variations in data formats, handling exceptions, and maintaining data standardization over time.
- Tools: ETL tools, scripting languages, data quality software.
- Best Practices: Creating data standardization guidelines, leveraging automation for repetitive tasks, and documenting data transformation processes.
- Considerations: Adapting standardization rules to specific data domains or business requirements.
3. Handling Missing Values:
- Description: Identifying and addressing missing or null values in a dataset.
- Example: A sales database contains missing entries for customer addresses, product prices, or order dates.
- Techniques: Imputing missing values, removing incomplete records, or flagging missing data for further analysis.
- Benefits: Improving data completeness, reducing bias in analysis, and ensuring the accuracy of statistical calculations.
- Challenges: Determining the cause of missing data, selecting appropriate imputation methods, and avoiding unintended biases.
- Tools: Statistical software, machine learning algorithms, data profiling tools.
- Best Practices: Understanding the nature of missing data, validating imputation methods, and documenting data quality issues.
- Considerations: Balancing the impact of missing data on analysis with the potential risks of imputation.
4. Data Transformation:
- Description: Converting data from one format, structure, or representation to another to meet specific requirements.
- Example: Converting raw transaction data into a summarized format for reporting or analysis.
- Techniques: Using data mapping, aggregation, or normalization to transform data elements.
- Benefits: Enabling data integration, supporting analytical queries, and preparing data for downstream processes.
- Challenges: Handling complex transformations, maintaining data lineage, and ensuring data consistency.
- Tools: ETL tools, scripting languages, data integration platforms.
- Best Practices: Defining clear transformation rules, validating transformation logic, and testing data quality after transformation.
- Considerations: Addressing the impact of data transformation on data governance, compliance, and security.
Additional Lake Formation configuration
Blueprints
Blueprints structurally sit on top of AWS Glue, using its service to fulfill tasks. Lake Formation is tightly integrated with AWS Glue. The benefits of this integration are observed across features such as blueprints. Blueprints are essentially templates for standard transformation activities that can involve multiple jobs to perform a specified set of actions. From these blueprints, you instantiate Lake Formation workflows. The workflows then perform jobs and tasks as defined.
Creating workflows
Workflows generate AWS Glue crawlers, jobs, and triggers to orchestrate the loading and updating of data. You can configure a workflow to run on demand or on a schedule. Workflows that you create in Lake Formation are visible in the AWS Glue console. Each node in a workflow is a job, crawler, or trigger. To monitor progress and troubleshoot, you can track the status of each node in the workflow.
Modern data architecture
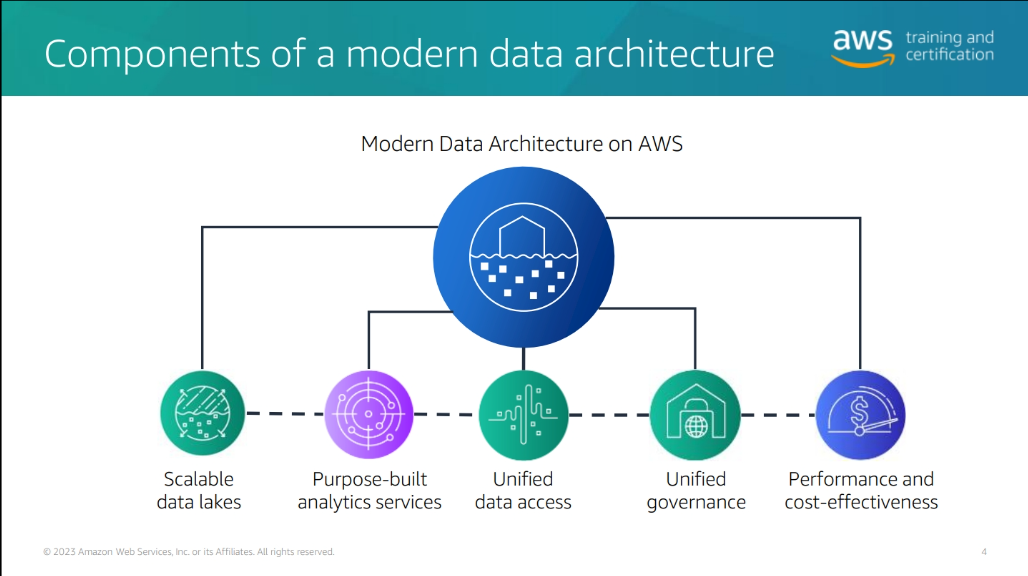
Scalable data lakes – This course has focused on the business value of data lakes and how to build data lakes with AWS Lake Formation. Business insight is driven by data of all types: structured, semi-structured, and unstructured. Organizations have large volumes of data generated continuously. To be able to extract value, data must be trusted and convenient to find by those roles that need access. Key AWS services include the following: • Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) – Highly durable, scalable, secure, fast, and inexpensive storage service.
• Lake Formation – Integrated data lake service that makes it convenient to ingest, clean, catalog, transform, and secure data and make it available for analysis and machine learning (ML).
• Amazon Athena – Interactive analytics service that makes it convenient to analyze data in Amazon S3 using Python or standard SQL