Building Data Analytics
Building Batch Data Analytics Solutions on AWS
In this guide, we'll explore how to build batch data analytics solutions using Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce). Amazon EMR is a cloud-based big data platform that allows you to process large datasets efficiently. We'll cover various modules to help you understand the key components and best practices for designing and implementing batch analytics solutions.
Module 1: Introduction to Amazon EMR
What is Amazon EMR?
Amazon EMR is a managed big data platform that simplifies the deployment and management of distributed data processing frameworks such as Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, and Apache Hive. It allows you to process large amounts of data using scalable compute resources.
Key Features of Amazon EMR:
- Scalability: EMR automatically scales resources based on workload requirements.
- Managed Clusters: EMR handles cluster provisioning, scaling, and termination.
- Integration with AWS Services: EMR integrates seamlessly with other AWS services like S3, DynamoDB, and Redshift.
- Security and Access Control: EMR provides security features such as encryption, IAM roles, and VPC integration.
File system options with EMR
- HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System) - default file system for Hadoop-based workloads
- EMRFS (EMR File System) - allows EMR clusters to read and write data directly to Amazon S3
Metadata storage solutions for Amazon EMR
-
Internal metastore – By default, Hive records metastore information in a MySQL database on the primary node's file system. When a cluster terminates, all cluster nodes shut down, including the primary node. When this happens, local data is lost because node file systems use ephemeral storage.
-
External Hive metastore – To use an external MySQL database or Amazon Aurora as your Hive metastore, you override the default configuration values for the metastore in Hive to specify the external database location, either on an Amazon RDS MySQL instance or an Amazon Aurora PostgreSQLinstance.
-
AWS Glue Data Catalog – With Amazon EMR version 5.8.0 or later, you can configure Hive to use the AWS Glue Data Catalog as its metastore. This configuration meets requirements for a persistent metastore or a metastore shared by different clusters, services, applications, or AWS accounts. You AWS CLI or API, you use the configuration classification for Hive to specify the Data Catalog.
Module 2: Data Analytics Pipeline Using Amazon EMR: Ingestion and Storage
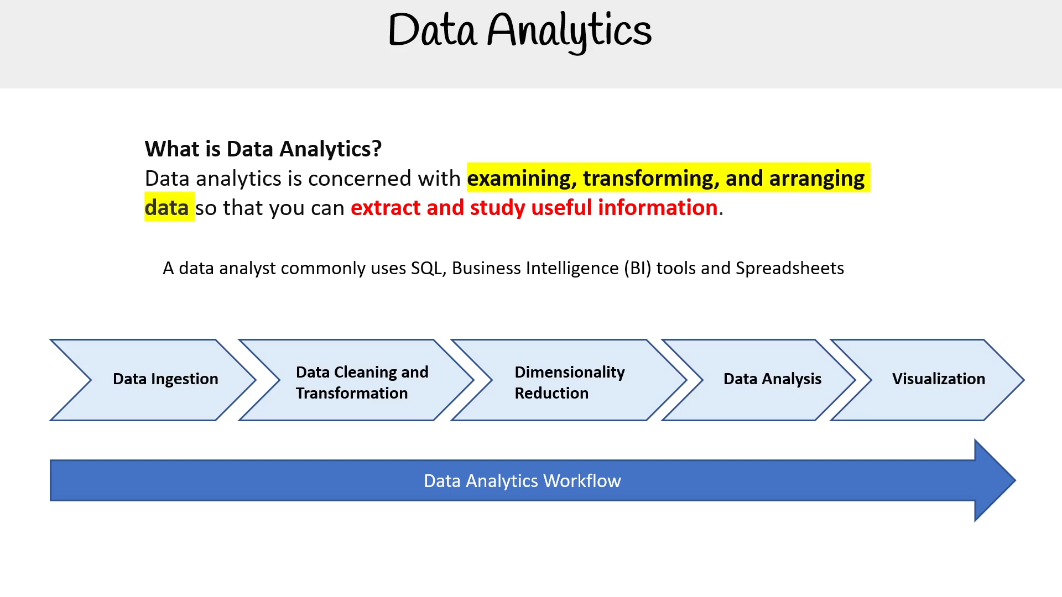
Data Ingestion:
- Use Amazon S3 to store raw data files.
- Set up EMR clusters to ingest data from S3 buckets.
- Consider using AWS Glue for ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tasks.
Data Storage:
- Leverage Amazon S3 for durable and scalable storage.
- Use EMRFS (EMR File System) for efficient data access from EMR clusters.
Format Supported
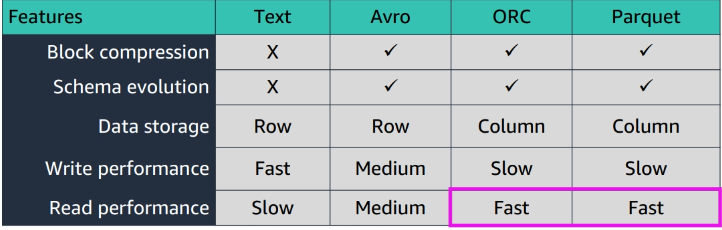
What is Parquet?
Parquet is a columnar storage file format that provides efficient storage and encoding of data. It is designed to work well with complex data types and nested data structures, making it suitable for big data processing frameworks like Apache Spark and Apache Hive.
Note imagine a table with 10k columns, and you only need 50 columns, parquet will only read the 50 columns you need, and not the entire table, which is a huge performance gain.
Data Compression
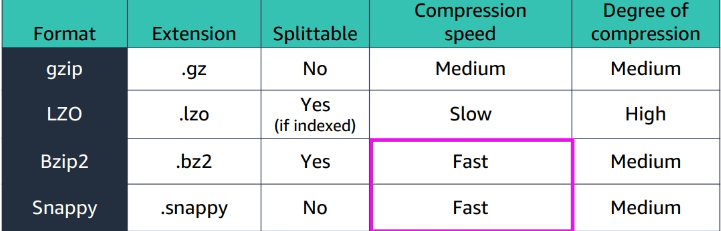
what to consider when choosing a compression format?
- storage cost
- bandwidth cost
- Compression ratio: The amount of compression achieved by the format.
- Compression speed: The time it takes to compress data.
- Decompression speed: The time it takes to decompress data.
- Compatibility with big data processing frameworks.
Module 3: High-Performance Batch Data Analytics Using Apache Spark on Amazon EMR
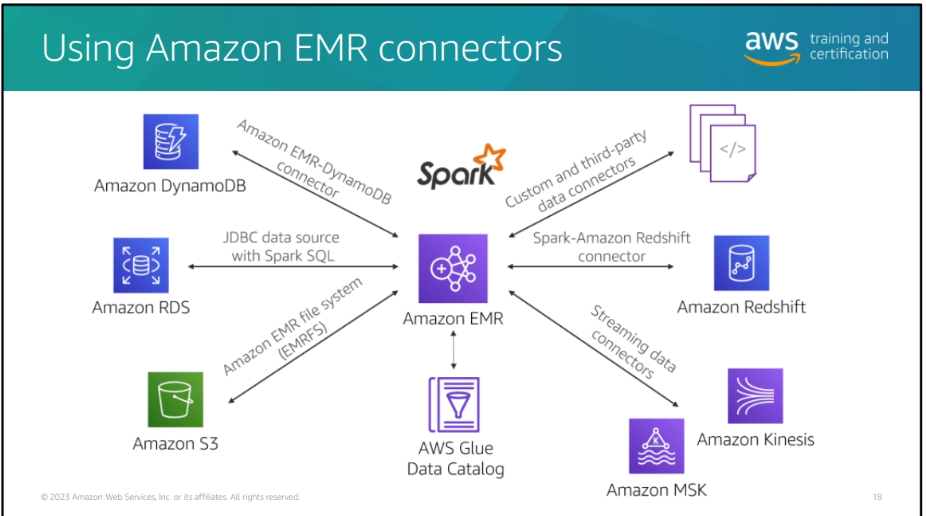
Spark on EMR: use cases
-
** Interactive Data Analysis**: Spark provides an interactive shell for ad-hoc data analysis and exploration.
-
ETL and Data Transformation: Use Spark to process and transform large datasets for downstream analytics.
-
Machine Learning: Leverage Spark's machine learning libraries for building and training predictive models.
-
Graph Processing: Analyze and process graph data using Spark's graph processing capabilities.
Apache Spark Overview:
- Spark is an open-source, in-memory data processing framework.
- EMR supports Spark for high-performance batch analytics.
- Use Spark for data transformation, machine learning, and graph processing.
Benefits of Spark on EMR:
-
In-Memory Processing: Spark utilizes in-memory caching for faster data processing.
-
Distributed Computing: Spark distributes data processing tasks across a cluster of nodes.
-
Developer Productivity: Spark provides high-level APIs for Python, Scala, and Java.
Spark features on Amazon EMRo
-
EMRFS s3-optimized committer: The EMRFS S3-optimized committer is a new output committer for Apache Spark that improves write performance when writing to S3.
-
Spark web UI: The Spark web UI is a web-based tool for monitoring and debugging Spark applications. You can use the Spark web UI to view information about your Spark application, such as the application's executors, jobs, stages, and tasks.
-
Aamazon EMR on EKS: Amazon EMR on EKS is a deployment option for Amazon EMR that allows you to run Apache Spark on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS). Amazon EMR on EKS runs the open-source big data frameworks on Amazon EKS to take advantage of the scalability, elasticity, and flexibility of Kubernetes.
-
AWS Glue Data Catalog: The AWS Glue Data Catalog is a fully managed, Apache Hive-compatible metadata catalog that makes it easy to discover, prepare, and store data. The AWS Glue Data Catalog is used by AWS Glue to store table which are for Spark SQL queries, and is used by Amazon EMR to store table metadata for Spark SQL queries.
Spark Components:
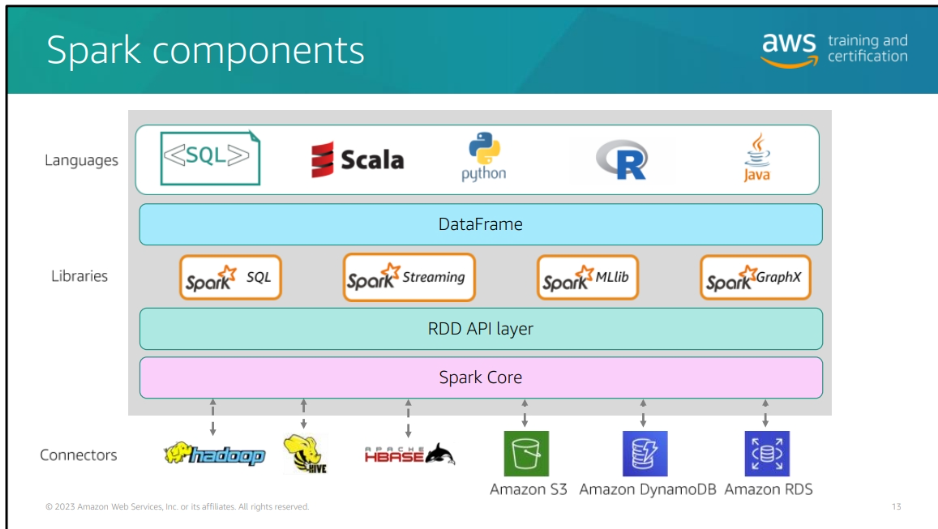
-
Spark Core: The foundation of the Spark platform, providing distributed task dispatching, scheduling, and basic I/O functionalities.
-
Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs): A fundamental data structure in Spark that represents a collection of elements distributed across multiple nodes.
-
Spark SQL: Provides a DataFrame API for working with structured data and SQL queries.
-
Spark Streaming: Enables real-time stream processing and integration with other data sources.
-
MLlib (Machine Learning Library): A scalable machine learning library for building and training machine learning models.
-
GraphX: A graph processing library for analyzing and processing graph data.
-
connectors: Spark provides connectors for integrating with various data sources such as Amazon S3, HDFS, JDBC, and more.
Setting Up Spark on EMR:
- Create an EMR cluster with Spark installed.
- Optimize Spark configurations for performance.
- Develop Spark applications using PySpark or Scala.
Module 4: Processing and Analyzing Batch Data with Amazon EMR and Apache Hive
Apache Hive:
- Hive is a data warehousing and SQL-like query language for Hadoop.
- Use Hive for batch processing and querying large datasets.
- Define tables, partitions, and views in Hive.
Integrating Hive with EMR:
- Configure Hive on your EMR cluster.
- Write HiveQL queries to analyze data.
- Optimize Hive performance by tuning settings.
Batch Data Processing with Hive SQL:
- Use Hive to process and analyze large datasets.
- Write SQL-like queries to perform data transformations.
- Leverage Hive's partitioning and bucketing for efficient processing.
Benefits of Hbase on EMR:
-
Fast Query Execution: Hive optimizes queries for efficient execution on EMR clusters.
-
Scalability: Hive can handle large-scale data processing and analytics.
-
Fault Tolerance: EMR provides fault-tolerant infrastructure for Hive processing.
Module 5: Serverless Data Processing
You can use serverless services, practices, and strategies to build more agile applications that help you innovate and respond to change faster. AWS handles infrastructure management tasks, such as capacity provisioning and patching, so you can focus on writing code that serves your customers. This module explores how serverless technology can support data processing, cataloging, and analytics at scale.
- Move from idea to market faster – By eliminating operational overhead, your teams can release quickly, get feedback, and iterate to get to market faster.
- Adapt at scale – With technologies that automatically scale from zero to peak demands, you can adapt to customer needs faster than ever.
- Build better applications with less effort – Serverless applications have built-in service integrations. You can focus on building your application instead of configuring it.
- Pay for use – Serverless has a pay-for-value billing model. You never pay for over-provisioning, and resource use is optimized on your behalf.
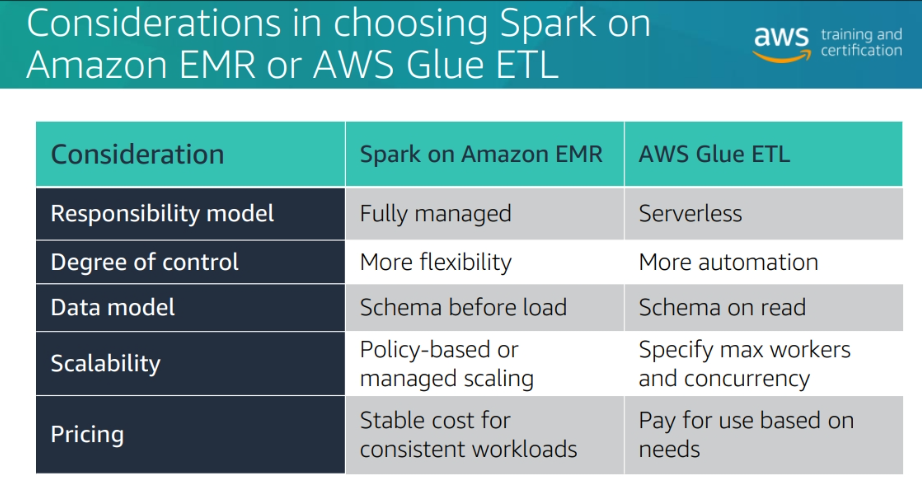
Module 6: Security and Monitoring of Ama zon EMR Clusters
Security Best Practices:
- Secure EMR clusters using IAM roles and policies.
- Enable encryption for data at rest and in transit.
- Implement network security using VPCs and security groups.
Monitoring and Logging:
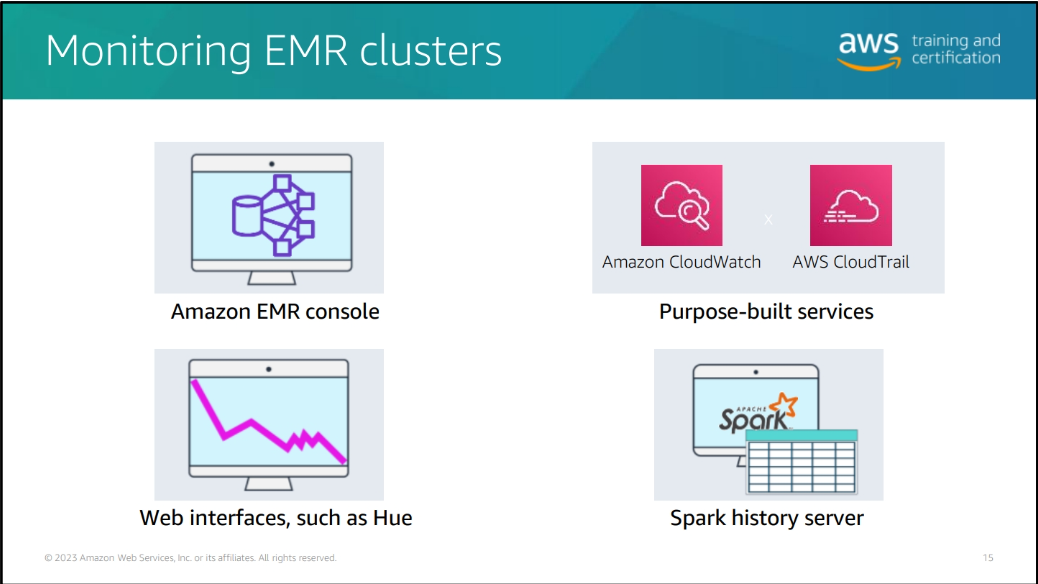
- Use Amazon CloudWatch for monitoring EMR clusters.
- Monitor resource utilization, job progress, and failures.
- Set up logging to track cluster activities.
Module 7: Designing Batch Analytics Solutions
Architectural Considerations:
- Choose the right EMR instance types based on workload.
- Design fault-tolerant and scalable architectures.
- Consider data partitioning and bucketing for efficient processing.
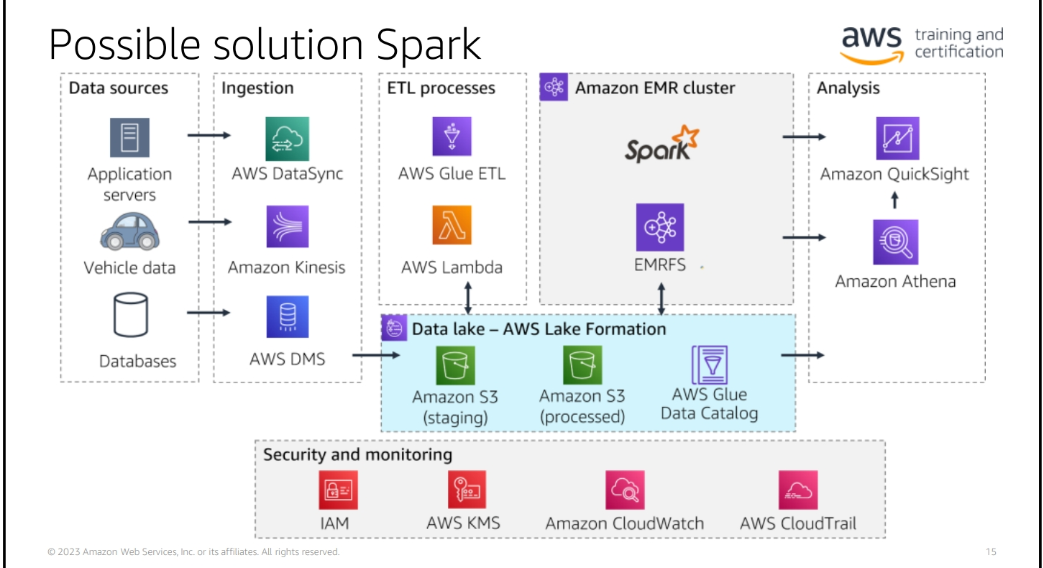
Module B: Developing Modern Data Architectures on AWS
Beyond EMR:
- Explore other AWS services like Amazon Redshift, Amazon Athena, and AWS Glue.
- Combine EMR with serverless services for comprehensive data solutions.
Feel free to expand on each section with additional details, examples, and practical use cases. If you have any specific questions or need further clarification, feel free to ask! 🚀🔍