MLOPS Engineering
MLOps Engineering
Objective
Initial MlOps Engineering
- Explain the benefits of MLOps.
- Compare and contrast DevOps and MLOps.
- Set up experimentation environments for MLOps with Amazon SageMaker.
- Evaluate the security and governance requirements for a machine learning (ML) use case.
Repeatable MLOps
-
Explain best practices for MLOps.
-
Describe three options for Creating a CI/CD Pipeline for ML.
Reliable MLOps
-
Recommend best practices for monitoring and troubleshooting ML models in production.
-
Demonstrate how to use Amazon SageMaker Model Monitor to monitor ML models in production.
-
Demonstrate how to automate an ML solution
Considerations and Challenges Operations ML
MLOps—a combination of Machine Learning and Operations—combines people, technology, and processes to deliver collaborative ML solutions.
This are more important than the technical aspects of MLOps.
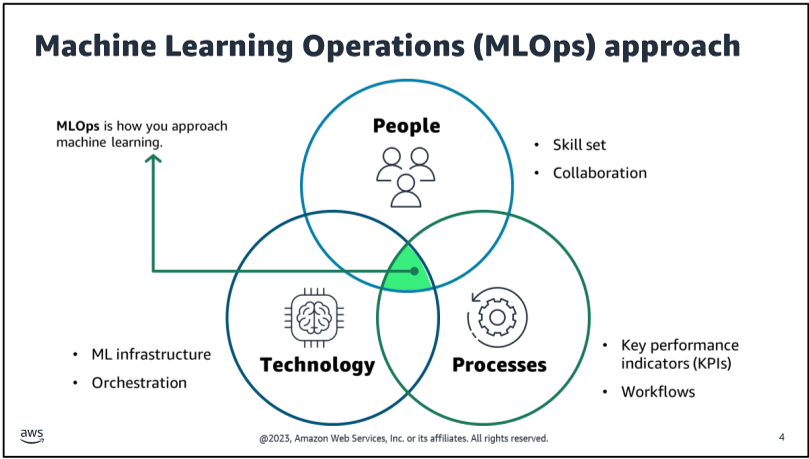
Why does ML workloads not make it to production?
It might be because a lot of the focus when designing and implementing an ML workload is on the function of the model. The focus is on getting the model to work in a development environment. There is often less focus on operating the model and making it accessible and reliable for users after it is trained.
ML Lifecycle
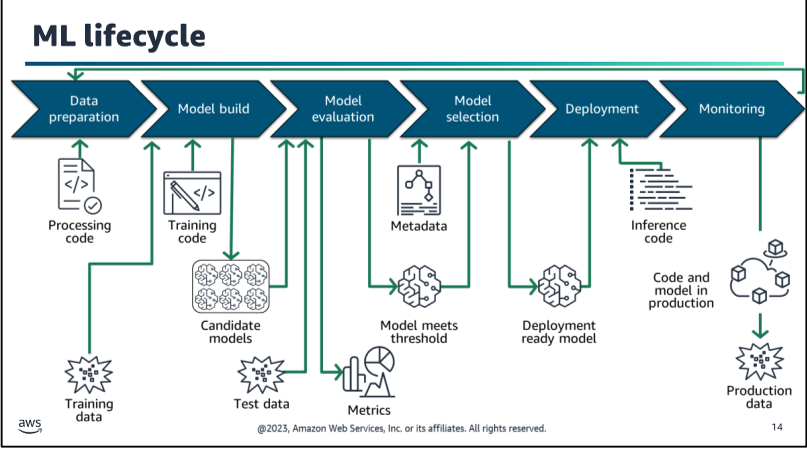
For more Explanation Refer back to
Machine Learning Pipeline on AWSMachine Learning Pipeline on AWSMachine Learning Pipeline on AWS Course Objectives - Select and justify the appropriate ML approach to a problem - Build ,train ,evaluate and deploy and fine-tune and ML model - Apply the steps of the Ml pipeline to solve the problem - Describe Best practices for training and deploying ML models pipeline in AWS - Identify the steps to apply the ML to business problems Course Outline Module 1: Introduction to Machine Learning and Ml Pipeline Data + Algorithm + Time = Model Inferenc
Consideration for MLOps
-
Consisitency: use the same tools and processes for training, deploying, and monitoring models.
-
Reproducibility: ensure that the results of a model can be reproduced.
-
Scalability: scale the model to handle the expected load.
-
Auditability: track the lineage of the model and the data used to train it.
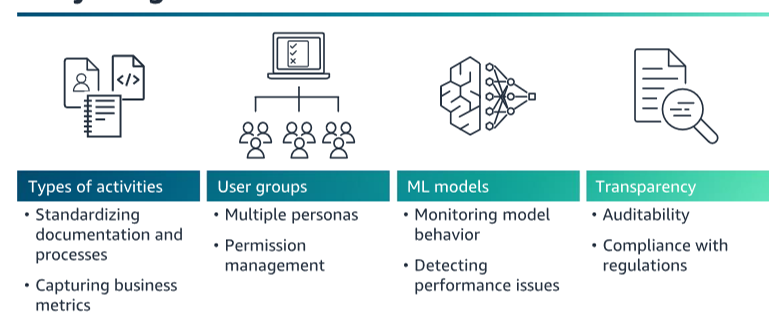
Why ML governance
Sage Maker
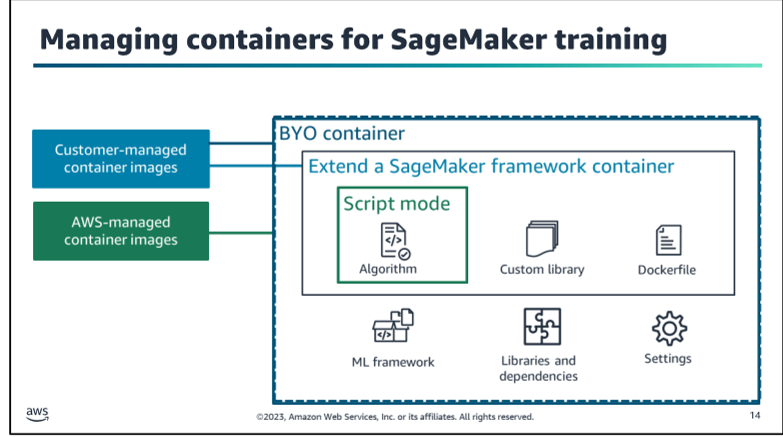
Important to know BYOC (Bring Your Own Container) and BYOM (Bring Your Own Model) are two important concepts in Amazon SageMaker. BYOC allows you to use your own Docker container to train and deploy models in Amazon SageMaker. BYOM allows you to use your own machine learning model to train and deploy models in Amazon SageMaker.
More Details
Parctical Data ScienceParctical Data SciencePractical Data Science Common ML use cases - Classification: Predicting a category - Regression: Predicting a number - Clustering: Finding groups in data - Anomaly detection: Finding outliers ML model benefits identify patterns**: ML models can identify patterns in data that humans can't Minimize human error**: ML models can make predictions without human intervention Can become more accurate over time**: ML models can learn from new data and improve their predictions variety of data

Reaptable MLOps Orchestration in AWS
-
Data Ingestion and Preparation:
- AWS Services: Amazon S3, AWS Glue, Amazon Athena, AWS Lake Formation
- Reaptable leverages AWS services to ingest and prepare data from various sources, such as databases, data lakes, and streaming data.
- AWS Glue is used for data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) processes, while Amazon Athena enables querying and analyzing data stored in Amazon S3.
- AWS Lake Formation simplifies data lake management and governance.
-
Model Training:
- AWS Services: Amazon SageMaker, AWS Batch, AWS Lambda
- Amazon SageMaker is the primary service for building, training, and deploying ML models.
- AWS Batch is used for running batch training jobs, while AWS Lambda enables serverless model training for specific use cases.
- Reaptable integrates with SageMaker to manage the training process, including data preprocessing, hyperparameter tuning, and distributed training.
-
Model Deployment and Serving:
- AWS Services: Amazon SageMaker, AWS Lambda, Amazon ECS, Amazon EKS
- Trained models are deployed using Amazon SageMaker or containerized services like AWS Lambda, Amazon ECS, or Amazon EKS, depending on the use case and scalability requirements.
- Reaptable simplifies the deployment process, including model packaging, scaling, and monitoring.
-
Model Monitoring and Management:
- AWS Services: Amazon SageMaker Model Monitor, AWS CloudWatch, AWS CloudTrail
- Amazon SageMaker Model Monitor is used for monitoring model performance, data drift, and other quality metrics.
- AWS CloudWatch and CloudTrail provide logging, monitoring, and auditing capabilities for the entire MLOps pipeline.
- Reaptable integrates with these services to enable continuous monitoring, model retraining, and version control.
-
Orchestration and Automation:
- AWS Services: AWS Step Functions, AWS Lambda, Amazon EventBridge
- AWS Step Functions is a key service for orchestrating the ML workflow, including data processing, model training, deployment, and monitoring.
- AWS Lambda is used for running serverless functions as part of the workflow.
- Amazon EventBridge enables event-driven automation and integration with other AWS services.
- Reaptable provides a user-friendly interface and abstractions for defining and managing ML workflows using these services.
-
Infrastructure as Code (IaC):
- AWS Services: AWS CloudFormation, AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK)
- Reaptable leverages IaC principles to provision and manage the required AWS resources for the MLOps pipeline.
- AWS CloudFormation and AWS CDK are used to define and deploy the infrastructure stack, enabling reproducibility and scalability.
-
Security and Governance:
- AWS Services: AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), AWS Key Management Service (KMS), AWS Security Hub, AWS Config
- Reaptable integrates with AWS security and governance services to ensure proper access control, data encryption, continuous compliance monitoring, and configuration management.
- AWS IAM is used for role-based access control, while AWS KMS provides key management and data encryption capabilities.
Reaptable MLOps Orchestration in AWS focuses on leveraging a wide range of AWS services to streamline and automate the entire ML lifecycle, from data ingestion to model deployment and monitoring. It provides a unified platform for managing ML workflows, ensuring scalability, reproducibility, and governance across the ML pipeline.
Module 5: Reliable MLOps, Scaling, and Testing
-
Testing and Monitoring:
- Implement comprehensive testing strategies, including unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests.
- Set up monitoring and logging systems to track the performance, accuracy, and reliability of your ML models in production.
- Leverage AWS services like Amazon CloudWatch and AWS Lambda for monitoring and automated testing.
-
Scaling and Performance:
- Understand the scalability and performance requirements of your ML workloads.
- Leverage AWS services like Amazon SageMaker, AWS Batch, and AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) for scalable training and inference.
- Optimize model serving through techniques like batching, caching, and auto-scaling.
-
Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD):
- Implement CI/CD pipelines for automating the build, test, and deployment processes of your ML systems.
- Use AWS CodePipeline, AWS CodeBuild, and AWS CodeDeploy for seamless integration and deployment.
- Automate model retraining, evaluation, and deployment to production environments.
-
Reproducibility and Versioning:
- Maintain reproducibility by versioning data, code, and model artifacts using tools like Git and AWS CodeCommit.
- Leverage AWS CodeArtifact or Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) for storing and managing artifacts.
- Track model lineage and experiment metadata using tools like MLflow or Amazon SageMaker Model Registry.
-
Infrastructure as Code (IaC):
- Adopt IaC principles to manage and provision AWS resources consistently and reliably.
- Use AWS CloudFormation or Terraform to define and manage your ML infrastructure as code.
Suggested Project Structure:
my-ml-project/
├── data/
│ ├── raw/
│ ├── processed/
│ └── ...
├── models/
│ ├── model_definitions/
│ ├── model_artifacts/
│ └── ...
├── tests/
│ ├── unit/
│ ├── integration/
│ └── ...
├── src/
│ ├── data/
│ ├── models/
│ ├── utils/
│ └── ...
├── pipelines/
│ ├── train.py
│ ├── deploy.py
│ └── ...
├── infrastructure/
│ ├── cloudformation/
│ ├── terraform/
│ └── ...
├── requirements.txt
├── README.md
└── ...
This structure separates concerns and promotes modularity, making it easier to scale and maintain your ML project. The data/ directory contains raw and processed data, models/ holds model definitions and artifacts, tests/ includes unit and integration tests, src/ contains the source code, pipelines/ manages training and deployment scripts, and infrastructure/ defines the infrastructure as code.
Remember, this is a general structure, and you may need to adapt it based on your specific project requirements and best practices.
AWS Reliable MLOps Monitoring
-
Model Drift Detection: One of the key aspects of AWS Reliable MLOps Monitoring is detecting model drift. Model drift occurs when the statistical properties of the input data or the relationship between the input data and target variable change over time, leading to a degradation in the model's performance. AWS Reliable MLOps Monitoring helps identify these drifts by continuously monitoring the input data, model predictions, and other relevant metrics.
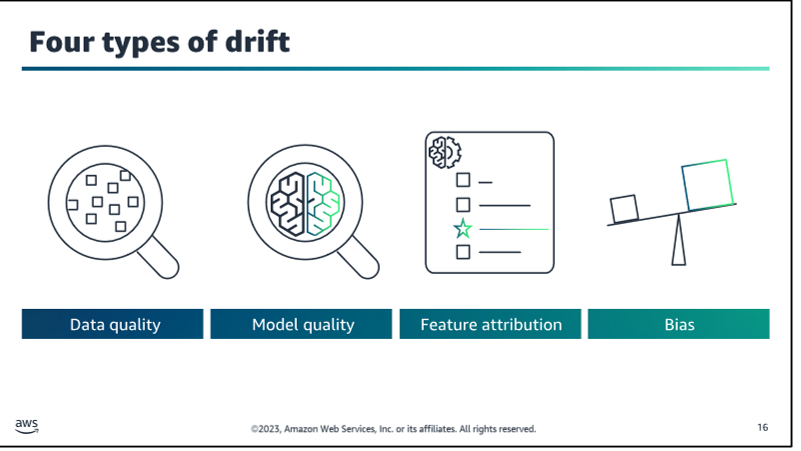
-
Data Quality Monitoring: Another crucial aspect is monitoring the quality of the input data used for making predictions. AWS Reliable MLOps Monitoring helps identify issues such as data drift (changes in the distribution of input data), missing values, outliers, and other data quality problems that can negatively impact the model's performance.
-
Performance Monitoring: AWS Reliable MLOps Monitoring also involves monitoring the performance of the deployed ML models in production. This includes tracking metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and other relevant performance indicators to ensure that the models are meeting the desired performance levels.
-
Automated Retraining and Deployment: In cases where model drift or performance degradation is detected, AWS Reliable MLOps Monitoring can trigger automated retraining and deployment processes. This ensures that the ML models are updated and optimized to maintain their performance and accuracy over time.
-
Explainability and Bias Monitoring: AWS Reliable MLOps Monitoring also focuses on monitoring the explainability and fairness of ML models. It helps identify potential biases and ensures that the models are making decisions in a transparent and unbiased manner.
-
Operational Monitoring: In addition to monitoring the ML models themselves, AWS Reliable MLOps Monitoring also includes operational monitoring of the underlying infrastructure, such as computing resources, storage, and networking components, to ensure the smooth and reliable operation of the ML systems.
The importance of AWS Reliable MLOps Monitoring lies in its ability to maintain the reliability, accuracy, and performance of ML models in production environments. Without proper monitoring and management, ML models can quickly become outdated or biased, leading to suboptimal or even harmful decision-making. By incorporating AWS Reliable MLOps Monitoring into the MLOps workflow, organizations can ensure that their ML systems remain reliable, efficient, and trustworthy over time.
Summary Achieving MLOps Maturity with AWS: A Guide to Streamlining Machine Learning Operations
Machine Learning Operations (MLOps) is an emerging discipline that aims to bridge the gap between data science and software engineering, enabling organizations to efficiently deploy, manage, and maintain machine learning (ML) models in production environments. In this blog post, we'll explore the key concepts and best practices for achieving MLOps maturity using Amazon Web Services (AWS) and its powerful tools, such as Amazon SageMaker.
The Journey to MLOps Maturity AWS outlines four levels of MLOps maturity: initial, repeatable, reliable, and scalable. Each level represents a progressive step towards a more streamlined and efficient ML workflow.
-
Initial MLOps: At this stage, data science and IT teams work in silos, with limited collaboration and cross-training. Data processing, model training, and deployment are primarily manual processes.
-
Repeatable MLOps: This phase marks the beginning of true MLOps adoption. Teams start collaborating with shared goals, automating data pipelines, and establishing defined paths for model experimentation and deployment.
-
Reliable MLOps: Cross-functional teams emerge, with improved data governance, integrated ML pipelines, and automated model validation. Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipelines are implemented, along with monitoring and logging for models, workloads, and pipelines.
-
Scalable MLOps: At the pinnacle of MLOps maturity, organizations establish well-defined processes, share best practices, and leverage templatization to speed up new solution development. Customized SageMaker project templates enforce organizational standards and automate the creation of secure MLOps environments.
Building MLOps into Your ML Solutions To raise your organization's MLOps maturity level, AWS recommends the following approaches:
-
Start small and iterate: Gradually introduce MLOps practices into your existing workflows, rather than attempting a complete overhaul.
-
Embrace "everything-as-code": Adopt an infrastructure-as-code approach to ensure repeatability, consistency, and governance across your ML pipelines.
-
Leverage ML-specific inputs, outputs, and artifacts: Maintain lineage for models, data, and pipelines to enable traceability and reproducibility.
-
Integrate SageMaker features and services: Utilize SageMaker's built-in capabilities, such as the Model Registry and Feature Store, to streamline model management and feature engineering.
-
Implement a Model Registry: Centralize model management, versioning, and deployment within your ML pipelines.
-
Explore the Feature Store: Store, share, and manage ML model features for training and inference, improving collaboration and reusability.
By following these guidelines and leveraging AWS's powerful MLOps tools, organizations can achieve a higher level of maturity, streamlining their ML operations and maximizing the value derived from their data and models.